This document is also available as
PostScript
and
DVI,
- RS-00-52
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Claude Crépeau, Frédéric
Légaré, and Louis Salvail.
How to Convert a Flavor of Quantum Bit Commitment.
December 2000.
24 pp. Appears in Pfitzmann, editor, Advances in Cryptology:
International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic
Techniques, EUROCRYPT '01 Proceedings, LNCS 2045, 2001, pages 60-77.
Abstract: In this paper we show how to convert a statistically
binding but computationally concealing quantum bit commitment scheme into a
computationally binding but statistically concealing scheme. For a security
parameter 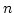 , the construction of the statistically concealing scheme
requires , the construction of the statistically concealing scheme
requires 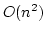 executions of the statistically binding scheme. As a
consequence, statistically concealing but computationally binding quantum bit
commitments can be based upon any family of quantum one-way functions. Such a
construction is not known to exist in the classical world. executions of the statistically binding scheme. As a
consequence, statistically concealing but computationally binding quantum bit
commitments can be based upon any family of quantum one-way functions. Such a
construction is not known to exist in the classical world.
- RS-00-51
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Peter D. Mosses.
CASL for CafeOBJ Users.
December 2000.
25 pp. Appears in Futatsugi, Nakagawa and Tamai, editors, CAFE:
An Industrial-Strength Algebraic Formal Method, 2000, chapter 6, pages
121-144.
Abstract: CASL is an expressive language for the algebraic
specification of software requirements, design, and architecture. It has been
developed by an open collaborative effort called CoFI (Common Framework
Initiative for algebraic specification and development). CASL combines the
best features of many previous main-stream algebraic specification languages,
and it should provide a focus for future research and development in the use
of algebraic techniques, as well facilitating interoperability of existing
and future tools.
This paper presents CASL for users of the CafeOBJ
framework, focussing on the relationship between the two languages. It first
considers those constructs of CafeOBJ that have direct counterparts in CASL,
and then (briefly) those that do not. It also motivates various CASL
constructs that are not provided by CafeOBJ. Finally, it gives a concise
overview of CASL, and illustrates how some CafeOBJ specifications may be
expressed in CASL.
- RS-00-50
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Peter D. Mosses.
Modularity in Meta-Languages.
December 2000.
19 pp. Appears in Despeyroux, editor, 2nd Workshop on Logical
Frameworks and Meta-Languages, LFM '00 Proceedings, 2000, pages 1-18.
Abstract: A meta-language for semantics has a high degree of
modularity when descriptions of individual language constructs can be
formulated independently using it, and do not require reformulation when new
constructs are added to the described language. The quest for modularity in
semantic meta-languages has been going on for more than two decades.
Here, most of the main meta-languages for operational, denotational, and
hybrid styles of semantics are compared regarding their modularity. A simple
bench-mark is used: describing the semantics of a pure functional language,
then extending the described language with references, exceptions, and
concurrency constructs. For each style of semantics, at least one of the
considered meta-languages appears to provide a high degree of modularity.
- RS-00-49
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Kohlenbach.
Higher Order Reverse Mathematics.
December 2000.
18 pp. To appear in S. G. Simpson (ed.), Reverse Mathematics.
Abstract: In this paper we argue for an extension of the second
order framework currently used in the program of reverse mathematics to
finite types. In particular we propose a conservative finite type extension
RCA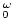 of the second order base system RCA of the second order base system RCA . By this
conservation nothing is lost for second order statements if we reason in
RCA . By this
conservation nothing is lost for second order statements if we reason in
RCA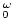 instead of RCA instead of RCA . However, the presence of finite types
allows to treat various analytical notions in a rather direct way, compared
to the encodings needed in RCA . However, the presence of finite types
allows to treat various analytical notions in a rather direct way, compared
to the encodings needed in RCA which are not always provably faithful in
RCA which are not always provably faithful in
RCA . Moreover, the language of finite types allows to treat many more
principles and gives rise to interesting extensions of the existing scheme of
reverse mathematics. We indicate this by showing that the class of principles
equivalent (over RCA . Moreover, the language of finite types allows to treat many more
principles and gives rise to interesting extensions of the existing scheme of
reverse mathematics. We indicate this by showing that the class of principles
equivalent (over RCA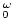 ) to Feferman's non-constructive ) to Feferman's non-constructive
 -operator forms a mathematically rich and very robust class. This is
closely related to a phenomenon in higher type recursion theory known as
Grilliot's trick. -operator forms a mathematically rich and very robust class. This is
closely related to a phenomenon in higher type recursion theory known as
Grilliot's trick.
- RS-00-48
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Marcin Jurdzinski and Jens Vöge.
A Discrete Stratety Improvement Algorithm for Solving Parity
Games.
December 2000.
31 pp. Extended abstract appears in Emerson and Sistla, editors, Computer-Aided Verification: 12th International Conference, CAV '00
Proceedings, LNCS 1855, 2000, pages 202-215.
Abstract: A discrete strategy improvement algorithm is given
for constructing winning strategies in parity games, thereby providing also a
new solution of the model-checking problem for the modal  -calculus.
Known strategy improvement algorithms, as proposed for stochastic games by
Hoffman and Karp in 1966, and for discounted payoff games and parity games by
Puri in 1995, work with real numbers and require solving linear programming
instances involving high precision arithmetic. In the present algorithm for
parity games these difficulties are avoided by the use of discrete vertex
valuations in which information about the relevance of vertices and certain
distances is coded. An efficient implementation is given for a strategy
improvement step. Another advantage of the present approach is that it
provides a better conceptual understanding and easier analysis of strategy
improvement algorithms for parity games. However, so far it is not known
whether the present algorithm works in polynomial time. The long standing
problem whether parity games can be solved in polynomial time remains open. -calculus.
Known strategy improvement algorithms, as proposed for stochastic games by
Hoffman and Karp in 1966, and for discounted payoff games and parity games by
Puri in 1995, work with real numbers and require solving linear programming
instances involving high precision arithmetic. In the present algorithm for
parity games these difficulties are avoided by the use of discrete vertex
valuations in which information about the relevance of vertices and certain
distances is coded. An efficient implementation is given for a strategy
improvement step. Another advantage of the present approach is that it
provides a better conceptual understanding and easier analysis of strategy
improvement algorithms for parity games. However, so far it is not known
whether the present algorithm works in polynomial time. The long standing
problem whether parity games can be solved in polynomial time remains open.
- RS-00-47
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Lasse R. Nielsen.
A Denotational Investigation of Defunctionalization.
December 2000.
50 pp. Presented at 16th Workshop on the Mathematical
Foundations of Programming Semantics, MFPS '00 (Hoboken, New Jersey, USA,
April 13-16, 2000).
Abstract: Defunctionalization has been introduced by John
Reynolds in his 1972 article Definitional Interpreters for Higher-Order
Programming Languages. Its goal is to transform a higher-order program into
a first-order one, representing functional values as data structures. Even
though defunctionalization has been widely used, we observe that it has never
been proven correct. We formalize defunctionalization denotationally for a
typed functional language, and we prove that it preserves the meaning of any
terminating program. Our proof uses logical relations.
- RS-00-46
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Zhe Yang.
Reasoning About Code-Generation in Two-Level Languages.
December 2000.
74 pp.
Abstract: This paper shows that two-level languages are not
only a good tool for describing code-generation algorithms, but a good tool
for reasoning about them as well. Common proof obligations of code-generation
algorithms in the form of two-level programs are captured by certain general
properties of two-level languages.
To prove that the generated code
behaves as desired, we use an erasure property, which equationally
relates the generated code to an erasure of the original two-level program in
the object language, thereby reducing the two-level proof obligation to a
simpler one-level obligation. To prove that the generated code satisfies
certain syntactic constraints, e.g., that it is in some normal form, we use a
type-preservation property for a refined type system that enforces
these constraints. Finally, to justify concrete implementations of
code-generation algorithms in one-level languages, we use a native
embedding of a two-level language into a one-level language.
We
present two-level languages with these properties both for a call-by-name
object language and for a call-by-value computational object language.
Indeed, it is these properties that guide our language design in the
call-by-value case. We consider two non-trivial applications: a one-pass
transformation into continuation-passing style and type-directed partial
evaluation for call-by-name and for call-by-value.
- RS-00-45
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ivan B. Damgård and Mads J. Jurik.
A Generalisation, a Simplification and some Applications of
Paillier's Probabilistic Public-Key System.
December 2000.
18 pp. Appears in Kim, editor, Fourth International Workshop on
Practice and Theory in Public Key Cryptography, PKC '01 Proceedings,
LNCS 1992, 2001, pages 119-136. This revised and extended report supersedes
the earlier BRICS report RS-00-5.
Abstract: We propose a generalisation of Paillier's
probabilistic public key system, in which the expansion factor is reduced and
which allows to adjust the block length of the scheme even after the public
key has been fixed, without loosing the homomorphic property. We show that
the generalisation is as secure as Paillier's original system.
We
construct a threshold variant of the generalised scheme as well as
zero-knowledge protocols to show that a given ciphertext encrypts one of a
set of given plaintexts, and protocols to verify multiplicative relations on
plaintexts.
We then show how these building blocks can be used for
applying the scheme to efficient electronic voting. This reduces dramatically
the work needed to compute the final result of an election, compared to the
previously best known schemes. We show how the basic scheme for a yes/no vote
can be easily adapted to casting a vote for up to 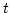 out of out of 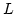 candidates.
The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to provide receipt-free
elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The scheme for 1 out of candidates.
The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to provide receipt-free
elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The scheme for 1 out of
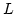 elections can be optimised such that for a certain range of parameter
values, a ballot has size only elections can be optimised such that for a certain range of parameter
values, a ballot has size only 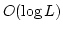 bits. bits.
- RS-00-44
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Bernd Grobauer and Zhe Yang.
The Second Futamura Projection for Type-Directed Partial
Evaluation.
December 2000.
Appears in Higher-Order and Symbolic Computation
14(2-3):173-219 (2001). This revised and extended report supersedes the
earlier BRICS report RS-99-40 which in turn was an extended version of
Lawall, editor, ACM SIGPLAN Workshop on Partial Evaluation and
Semantics-Based Program Manipulation, PEPM '00 Proceedings, 2000, pages
22-32.
Abstract: A generating extension of a program specializes the
program with respect to part of the input. Applying a partial evaluator to
the program trivially yields a generating extension, but specializing the
partial evaluator with respect to the program often yields a more efficient
one. This specialization can be carried out by the partial evaluator itself;
in this case, the process is known as the second Futamura projection.
We derive an ML implementation of the second Futamura projection for
Type-Directed Partial Evaluation (TDPE). Due to the differences between
`traditional', syntax-directed partial evaluation and TDPE, this derivation
involves several conceptual and technical steps. These include a suitable
formulation of the second Futamura projection and techniques for making TDPE
amenable to self-application. In the context of the second Futamura
projection, we also compare and relate TDPE with conventional offline partial
evaluation.
We demonstrate our technique with several examples,
including compiler generation for Tiny, a prototypical imperative language.
- RS-00-43
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Claus Brabrand, Anders Møller,
Mikkel Ricky Christensen, and Michael I. Schwartzbach.
PowerForms: Declarative Client-Side Form Field Validation.
December 2000.
21 pp. Appears in World Wide Web Journal, 4(3), 2000.
Abstract: All uses of HTML forms may benefit from validation of
the specified input field values. Simple validation matches individual values
against specified formats, while more advanced validation may involve
interdependencies of form fields.
There is currently no standard for
specifying or implementing such validation. Today, CGI programmers often use
Perl libraries for simple server-side validation or program customized
JavaScript solutions for client-side validation.
We present
PowerForms, which is an add-on to HTML forms that allows a purely declarative
specification of input formats and sophisticated interdependencies of form
fields. While our work may be seen as inspiration for a future extension of
HTML, it is also available for CGI programmers today through a preprocessor
that translates a PowerForms document into a combination of standard HTML and
JavaScript that works on all combinations of platforms and browsers.
The definitions of PowerForms formats are syntactically disjoint from the
form itself, which allows a modular development where the form is perhaps
automatically generated by other tools and the formats and interdependencies
are added separately.
- RS-00-42
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Claus Brabrand, Anders Møller, and
Michael I. Schwartzbach.
The <bigwig> Project.
December 2000.
25 pp. To appear in ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 2002.
Abstract: We present the results of the <bigwig> project,
which aims to design and implement a high-level domain-specific language for
programming interactive Web services. The World Wide Web has undergone an
extreme development since its invention ten years ago. A fundamental aspect
is the change from static to dynamic generation of Web pages. Generating Web
pages dynamically in dialogue with the client has the advantage of providing
up-to-date and tailor-made information. The development of systems for
constructing such dynamic Web services has emerged as a whole new research
area. The <bigwig> language is designed by analyzing its application
domain and identifying fundamental aspects of Web services. Each aspect is
handled by a nearly independent sublanguage, and the entire collection is
integrated into a common core language. The <bigwig> compiler uses the
available Web technologies as target languages, making <bigwig>
available on almost any combination of browser and server, without relying on
plugins or server modules.
- RS-00-41
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Nils Klarlund, Anders Møller, and
Michael I. Schwartzbach.
The DSD Schema Language and its Applications.
December 2000.
32 pp. Appears in Automated Software Engineering,
9(3):285-319,2002. Shorter version appears in Heimdahl, editor, 3rd
ACM SIGSOFT Workshop on on Formal Methods in Software Practice, FMSP '00
Proceedings, 2000 , pages 101-111.
Abstract: XML (eXtensible Markup Language), a linear syntax for
trees, has gathered a remarkable amount of interest in industry. The
acceptance of XML opens new venues for the application of formal methods such
as specification of abstract syntax tree sets and tree
transformations.
A user domain may be specified as a set of trees. For
example, XHTML is a user domain corresponding to the set of XML documents
that make sense as HTML. A notation for defining such a set of XML trees is
called a schema language. We believe that a useful schema notation must
identify most of the syntactic requirements that the documents in the user
domain follow; allow efficient parsing; be readable to the user; allow a
declarative default notation a la CSS; and be modular and extensible to
support evolving classes of XML documents.
In the present paper, we
give a tutorial introduction to the DSD (Document Structure Description)
notation as our bid on how to meet these requirements. The DSD notation was
inspired by industrial needs, and we show how DSDs help manage aspects of
complex XML software through a case study about interactive voice response
systems (automated telephone answering systems, where input is through the
telephone keypad or speech recognition).
The expressiveness of DSDs
goes beyond the DTD schema concept that is already part of XML. We advocate
the use of nonterminals in a top-down manner, coupled with boolean logic and
regular expressions to describe how constraints on tree nodes depend on their
context. We also support a general, declarative mechanism for inserting
default elements and attributes that is reminiscent of Cascading Style Sheets
(CSS), a way of manipulating formatting instructions in HTML that is built
into all modern browsers. Finally, we include a simple technique for evolving
DSDs through selective redefinitions. DSDs are in many ways much more
expressive than XML Schema (the schema language proposed by the W3C), but
their syntactic and semantic definition in English is only 1/8th the size.
Also, the DSD notation is self-describable: the syntax of legal DSD documents
and all static semantic requirements can be captured in a DSD document,
called the meta-DSD.
- RS-00-40
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Nils Klarlund, Anders Møller, and
Michael I. Schwartzbach.
MONA Implementation Secrets.
December 2000.
19 pp. Appears in International Journal of Foundations of
Computer Science, 13(4):571-586, 2002. Shorter version appears in Yu and
Paum, editors, Fifth International Conference on Implementation and
Application of Automata, CIAA '00 Pre-Proceedings, LNCS 2088, 2001, pages
182-194.
Abstract: The MONA tool provides an implementation of
automaton-based decision procedures for the logics WS1S and WS2S. It has been
used for numerous applications, and it is remarkably efficient in practice,
even though it faces a theoretically non-elementary worst-case complexity.
The implementation has matured over a period of six years. Compared to the
first naive version, the present tool is faster by several orders of
magnitude. This speedup is obtained from many different contributions working
on all levels of the compilation and execution of formulas. We present an
overview of MONA and a selection of implementation ``secrets'' that have been
discovered and tested over the years, including formula reductions,
DAGification, guided tree automata, three-valued logic, eager minimization,
BDD-based automata representations, and cache-conscious data structures. We
describe these techniques and quantify their respective effects by
experimenting with separate versions of the MONA tool that in turn omit each
of them.
- RS-00-39
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Anders Møller and Michael I.
Schwartzbach.
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine.
December 2000.
23 pp. Appears in ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming
Language Design and Implementation, PLDI '01 Proceedings, 2001 pp.
221-231.
Abstract: We present a new framework for verifying partial
specifications of programs in order to catch type and memory errors and check
data structure invariants. Our technique can verify a large class of data
structures, namely all those that can be expressed as graph types. Earlier
versions were restricted to simple special cases such as lists or trees. Even
so, our current implementation is as fast as the previous specialized
tools.
Programs are annotated with partial specifications expressed in
Pointer Assertion Logic, a new notation for expressing properties of the
program store. We work in the logical tradition by encoding the programs and
partial specifications as formulas in monadic second-order logic. Validity of
these formulas is checked by the MONA tool, which also can provide explicit
counterexamples to invalid formulas.
Other work with similar goals is
based on more traditional program analyses, such as shape analysis. That
approach requires explicit introduction of an appropriate operational
semantics along with a proof of correctness whenever a new data structure is
being considered. In comparison, our approach only requires the data
structure to be abstractly described in Pointer Assertion Logic.
- RS-00-38
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Bertrand Jeannet.
Dynamic Partitioning in Linear Relation Analysis: Application to
the Verification of Synchronous Programs.
December 2000.
44 pp.
Abstract: Linear relation analysis is an abstract
interpretation technique that computes linear constraints satisfied by the
numerical variables of a program. We apply it to the verification of
declarative synchronous programs. In this approach, state
partitioning plays an important role: on one hand the precision of the
results highly depends on the fineness of the partitioning; on the other
hand, a too much detailed partitioning may result in an exponential explosion
of the analysis. In this paper we propose to consider very general partitions
of the state space and to dynamically select a suitable partitioning
according to the property to be proved. The presented approach is quite
general and can be applied to other abstract interpretations.
- RS-00-37
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Thomas S. Hune, Kim G. Larsen, and Paul
Pettersson.
Guided Synthesis of Control Programs for a Batch Plant using
UPPAAL.
December 2000.
29 pp. Appears in Lai, editor, International Workshop in
Distributed Systems Validation and Verification. Held in conjunction with
20th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems
(ICDCS '2000), DSVV '00 Proceedings, 2000, pages E15-E22 and Nordic
Journal of Computing, 8(1):43-64, 2001.
Abstract: In this paper we address the problem of scheduling
and synthesizing distributed control programs for a batch production plant.
We use a timed automata model of the batch plant and the verification tool
Uppaal to solve the scheduling problem.
In modeling the plant, we aim
at a level of abstraction which is sufficiently accurate in order that
synthesis of control programs from generated timed traces is possible.
Consequently, the models quickly become too detailed and complicated for
immediate automatic synthesis. In fact, only models of plants producing two
batches can be analyzed directly! To overcome this problem, we present a
general method allowing the user to guide the model-checker according to
heuristically chosen strategies. The guidance is specified by augmenting the
model with additional guidance variables and by decorating transitions with
extra guards on these. Applying this method have made synthesis of control
programs feasible for a plant producing as many as 60 batches.
The
synthesized control programs have been executed in a physical plant. Besides
proving useful in validating the plant model and in finding some modeling
errors, we view this final step as the ultimate litmus test of our
methodology's ability to generate executable (and executing) code from basic
plant models.
- RS-00-36
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Rasmus Pagh.
Dispersing Hash Functions.
December 2000.
18 pp. Preliminary version appeared in Rolim, editor, 4th
International Workshop on Randomization and Approximation Techniques in
Computer Science, RANDOM '00, Proceedings in Informatics, 2000, pages
53-67.
Abstract: A new hashing primitive is introduced: dispersing
hash functions. A family of hash functions 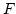 is dispersing if, for any set is dispersing if, for any set
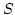 of a certain size and random of a certain size and random 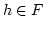 , the expected value of , the expected value of ![$\vert S\vert-\vert h[S]\vert$](img12.gif) is not much larger than the expectancy if
is not much larger than the expectancy if 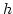 had been chosen at random from
the set of all functions. had been chosen at random from
the set of all functions.
We give tight, up to a logarithmic factor,
upper and lower bounds on the size of dispersing families. Such families
previously studied, for example universal families, are significantly larger
than the smallest dispersing families, making them less suitable for
derandomization. We present several applications of dispersing families to
derandomization (fast element distinctness, set inclusion, and static
dictionary initialization). Also, a tight relationship between dispersing
families and extractors, which may be of independent interest, is
exhibited.
We also investigate the related issue of program size for
hash functions which are nearly perfect. In particular, we exhibit a
dramatic increase in program size for hash functions more dispersing than a
random function.
- RS-00-35
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy and Lasse R. Nielsen.
CPS Transformation of Beta-Redexes.
December 2000.
12 pp. Appears in Sabry, editor, 3rd ACM SIGPLAN Workshop on
Continuations, CW '01 Proceedings, Association for Computing Machinery
(ACM) SIGPLAN Technical Report 545, 2001, pages 35-39.
Abstract: The extra compaction of Sabry and Felleisen's
transformation is due to making continuations occur first in CPS terms and
classifying more redexes as administrative. We show that the extra compaction
is actually independent of the relative positions of values and continuations
and furthermore that it is solely due to a context-sensitive transformation
of beta-redexes. We stage the more compact CPS transformation into a
first-order uncurrying phase and a context-insensitive CPS transformation. We
also define a context-insensitive CPS transformation that is just as compact.
This CPS transformation operates in one pass and is dependently typed.
- RS-00-34
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy and Morten Rhiger.
A Simple Take on Typed Abstract Syntax in Haskell-like
Languages.
December 2000.
25 pp. Appears in Kuchen and Ueda, editors, Fifth International
Symposium on Functional and Logic Programming, FLOPS '01 Proceedings,
LNCS 2024, 2001, pages 343-358.
Abstract: We present a simple way to program typed abstract
syntax in a language following a Hindley-Milner typing discipline, such as ML
and Haskell, and we apply it to automate two proofs about normalization
functions as embodied in type-directed partial evaluation for the simply
typed lambda calculus: (1) normalization functions preserve types and (2)
they yield long beta-eta normal forms.
- RS-00-33
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy and Lasse R. Nielsen.
A Higher-Order Colon Translation.
December 2000.
17 pp. Appears in Kuchen and Ueda, editors, Fifth International
Symposium on Functional and Logic Programming, FLOPS '01 Proceedings,
LNCS 2024, 2001, pages 78-91.
Abstract: A lambda-encoding such as the CPS transformation
gives rise to administrative redexes. In his seminal article ``Call-by-name,
call-by-value and the lambda-calculus'', 25 years ago, Plotkin tackled
administrative reductions using a so-called ``colon translation.'' 10 years
ago, Danvy and Filinski integrated administrative reductions in the CPS
transformation, making it operate in one pass. The technique applies to other
lambda-encodings (e.g., variants of CPS), but we do not see it used in
practice--instead, Plotkin's colon translation appears to be favored.
Therefore, in an attempt to link both techniques, we recast Plotkin's proof
of Indifference and Simulation to the higher-order specification of the
one-pass CPS transformation. To this end, we extend his colon translation
from first order to higher order.
- RS-00-32
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
John C. Reynolds.
The Meaning of Types -- From Intrinsic to Extrinsic Semantics.
December 2000.
35 pp. A shorter version of this report describing a more limited
language appears in Annabelle McIver and Carroll Morgan (eds.) Essays on
Programming Methodology, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2001.
Abstract: A definition of a typed language is said to be
``intrinsic'' if it assigns meanings to typings rather than arbitrary
phrases, so that ill-typed phrases are meaningless. In contrast, a definition
is said to be ``extrinsic'' if all phrases have meanings that are independent
of their typings, while typings represent properties of these
meanings.
For a simply typed lambda calculus, extended with recursion,
subtypes, and named products, we give an intrinsic denotational semantics and
a denotational semantics of the underlying untyped language. We then
establish a logical relations theorem between these two semantics, and show
that the logical relations can be ``bracketed'' by retractions between the
domains of the two semantics. From these results, we derive an extrinsic
semantics that uses partial equivalence relations.
- RS-00-31
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Bernd Grobauer and Julia L. Lawall.
Partial Evaluation of Pattern Matching in Strings, revisited.
November 2000.
48 pp. Appears in Nordic Journal of Computing, 8(4):437-462,
2001.
Abstract: Specializing string matchers is a canonical example
of partial evaluation. A naive implementation of a string matcher repeatedly
matches a pattern against every substring of the data string; this operation
should intuitively benefit from specializing the matcher with respect to the
pattern. In practice, however, producing an efficient implementation by
performing this specialization using standard partial-evaluation techniques
has been found to require non-trivial binding-time improvements. Starting
with a naive matcher, we thus present a derivation of a binding-time improved
string matcher. We prove its correctness and show that specialization with
respect to a pattern yields a matcher with code size linear in the length of
the pattern and running time linear in the length of its input. We then
consider several variants of matchers that specialize well, amongst them the
first such matcher presented in the literature, and we demonstrate how
variants can be derived from each other systematically.
- RS-00-30
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ivan B. Damgård and Maciej Koprowski.
Practical Threshold RSA Signatures Without a Trusted Dealer.
November 2000.
14 pp. Appears in Pfitzmann, editor, Advances in Cryptology:
International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic
Techniques, EUROCRYPT '01 Proceedings, LNCS 2045, 2001, pages 152-165.
Abstract: We propose a threshold RSA scheme which is as
efficient as the fastest previous threshold RSA scheme (by Shoup), but where
two assumptions needed in Shoup's and in previous schemes can be dropped,
namely that the modulus must be a product of safe primes and that a trusted
dealer generates the keys.
- RS-00-29
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Luigi Santocanale.
The Alternation Hierarchy for the Theory of  -lattices. -lattices.
November 2000.
44 pp. Extended abstract appears in Abstracts from the
International Summer Conference in Category Theory, CT2000, Como, Italy,
July 16-22, 2000. Appears in Theory and Applications of Categories,
9:166-197, 2002.
Abstract: The alternation hierarchy problem asks whether every
 -term, that is a term built up using also a least fixed point
constructor as well as a greatest fixed point constructor, is equivalent to a -term, that is a term built up using also a least fixed point
constructor as well as a greatest fixed point constructor, is equivalent to a
 -term where the number of nested fixed point of a different type is
bounded by a fixed number. -term where the number of nested fixed point of a different type is
bounded by a fixed number.
In this paper we give a proof that the
alternation hierarchy for the theory of  -lattices is strict, meaning
that such number does not exist if -lattices is strict, meaning
that such number does not exist if  -terms are built up from the basic
lattice operations and are interpreted as expected. The proof relies on the
explicit characterization of free -terms are built up from the basic
lattice operations and are interpreted as expected. The proof relies on the
explicit characterization of free  -lattices by means of games and
strategies. -lattices by means of games and
strategies.
- RS-00-28
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Luigi Santocanale.
Free  -lattices. -lattices.
November 2000.
51 pp. Short abstract appeared in Proceedings of Category Theory
99, Coimbra, Portugal, July 19-24, 1999. Full version appears in the
Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 168/2-3, pp. 227-264.
Abstract: A  -lattice is a lattice with the property that
every unary polynomial has both a least and a greatest fix-point. In this
paper we define the quasivariety of -lattice is a lattice with the property that
every unary polynomial has both a least and a greatest fix-point. In this
paper we define the quasivariety of  -lattices and, for a given partially
ordered set -lattices and, for a given partially
ordered set 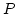 , we construct a , we construct a  -lattice -lattice 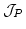 whose elements
are equivalence classes of games in a preordered class whose elements
are equivalence classes of games in a preordered class 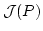 . We
prove that the . We
prove that the  -lattice -lattice 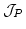 is free over the ordered set is free over the ordered set 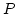 and that the order relation of
and that the order relation of
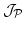 is decidable if the order
relation of is decidable if the order
relation of 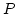 is decidable. By means of this characterization of free is decidable. By means of this characterization of free
 -lattices we infer that the class of complete lattices generates the
quasivariety of -lattices we infer that the class of complete lattices generates the
quasivariety of  -lattices. -lattices.
- RS-00-27
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Zoltán Ésik and Werner Kuich.
Inductive  -Semirings. -Semirings.
October 2000.
34 pp. To appear in Theoretical Computer Science.
Abstract: One of the most well-known induction principles in
computer science is the fixed point induction rule, or least pre-fixed point
rule. Inductive  -semirings are partially ordered semirings equipped with
a star operation satisfying the fixed point equation and the fixed point
induction rule for linear terms. Inductive -semirings are partially ordered semirings equipped with
a star operation satisfying the fixed point equation and the fixed point
induction rule for linear terms. Inductive  -semirings are extensions of
continuous semirings and the Kleene algebras of Conway and Kozen. -semirings are extensions of
continuous semirings and the Kleene algebras of Conway and Kozen.
We
develop, in a systematic way, the rudiments of the theory of inductive
 -semirings in relation to automata, languages and power series. In
particular, we prove that if -semirings in relation to automata, languages and power series. In
particular, we prove that if 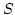 is an inductive is an inductive  -semiring, then so is
the semiring of matrices -semiring, then so is
the semiring of matrices
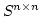 , for any integer , for any integer 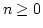 , and
that if , and
that if 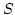 is an inductive is an inductive  -semiring, then so is any semiring of power
series -semiring, then so is any semiring of power
series
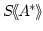 . As shown
by Kozen, the dual of an inductive . As shown
by Kozen, the dual of an inductive  -semiring may not be inductive. In
contrast, we show that the dual of an iteration semiring is an iteration
semiring. Kuich proved a general Kleene theorem for continuous semirings, and
Bloom and Ésik proved a Kleene theorem for all Conway semirings. Since
any inductive -semiring may not be inductive. In
contrast, we show that the dual of an iteration semiring is an iteration
semiring. Kuich proved a general Kleene theorem for continuous semirings, and
Bloom and Ésik proved a Kleene theorem for all Conway semirings. Since
any inductive  -semiring is a Conway semiring and an iteration semiring,
as we show, there results a Kleene theorem applicable to all inductive -semiring is a Conway semiring and an iteration semiring,
as we show, there results a Kleene theorem applicable to all inductive
 -semirings. We also describe the structure of the initial inductive -semirings. We also describe the structure of the initial inductive
 -semiring and conjecture that any free inductive -semiring and conjecture that any free inductive  -semiring may be
given as a semiring of rational power series with coefficients in the initial
inductive -semiring may be
given as a semiring of rational power series with coefficients in the initial
inductive  -semiring. We relate this conjecture to recent axiomatization
results on the equational theory of the regular sets. -semiring. We relate this conjecture to recent axiomatization
results on the equational theory of the regular sets.
- RS-00-26
-
PostScript,
PDF.
František Capkovic.
Modelling and Control of Discrete Event Dynamic Systems.
October 2000.
58 pp.
Abstract: Discrete event dynamic systems (DEDS) in general are
investigated as to their analytical models most suitable for control purposes
and as to the analytical methods of the control synthesis. The possibility of
utilising both the selected kind of Petri nets and the oriented graphs on
this way is pointed out. Because many times the control task specifications
(like criteria, constraints, special demands, etc.) are given only verbally
or in another form of non analytical terms, a suitable knowledge
representation about the specifications is needed. Special kinds of Petri
nets (logical, fuzzy) are suitable on this way too. Hence, the
knowledge-based control synthesis of DEDS can also be examined. The developed
graphical tools for model drawing and testing as well as for the automated
knowledge-based control synthesis are described and illustratively
presented.
Two approaches to modelling and control synthesis based on
oriented graphs are developed. They are suitable when the system model is
described by the special kind of Petri nets - state machines. At the control
synthesis the first of them is straightforward while the second one combines
both the straight-lined model dynamics development (starting from the given
initial state towards the prescribed terminal one) and the backtracking model
dynamics development.
- RS-00-25
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Zoltán Ésik.
Continuous Additive Algebras and Injective Simulations of
Synchronization Trees.
September 2000.
41 pp. Appears in Journal of Logic and Computation,
12(2):271-300, 2002.
Abstract: The (in)equational properties of the least fixed
point operation on (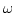 -)continuous functions on ( -)continuous functions on (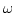 -)complete
partially ordered sets are captured by the axioms of (ordered) iteration
algebras, or iteration theories. We show that the inequational laws of the
sum operation in conjunction with the least fixed point operation in
continuous additive algebras have a finite axiomatization over the
inequations of ordered iteration algebras. As a byproduct of this relative
axiomatizability result, we obtain complete infinite inequational and finite
implicational axiomatizations. Along the way of proving these results, we
give a concrete description of the free algebras in the corresponding variety
of ordered iteration algebras. This description uses injective simulations of
regular synchronization trees. Thus, our axioms are also sound and complete
for the injective simulation (resource bounded simulation) of (regular)
processes. -)complete
partially ordered sets are captured by the axioms of (ordered) iteration
algebras, or iteration theories. We show that the inequational laws of the
sum operation in conjunction with the least fixed point operation in
continuous additive algebras have a finite axiomatization over the
inequations of ordered iteration algebras. As a byproduct of this relative
axiomatizability result, we obtain complete infinite inequational and finite
implicational axiomatizations. Along the way of proving these results, we
give a concrete description of the free algebras in the corresponding variety
of ordered iteration algebras. This description uses injective simulations of
regular synchronization trees. Thus, our axioms are also sound and complete
for the injective simulation (resource bounded simulation) of (regular)
processes.
- RS-00-24
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Claus Brabrand and Michael I.
Schwartzbach.
Growing Languages with Metamorphic Syntax Macros.
September 2000.
22 pp. Appears in Thiemann, editor, ACM SIGPLAN Workshop on
Partial Evaluation and Semantics-Based Program Manipulation, PEPM '02
Proceedings, 2002, pages 31-40.
Abstract: ``From now on, a main goal in designing a
language should be to plan for growth.'' Guy Steele: Growing a Language,
OOPSLA'98 invited talk.
We present our experiences with a syntax
macro language augmented with a concept of metamorphisms. We claim this
forms a general abstraction mechanism for growing (domain-specific)
extensions of programming languages.
Our syntax macros are similar to
previous work in that the compiler accepts collections of grammatical rules
that extend the syntax in which a subsequent program may be written. We
exhibit how almost arbitrary extensions can be defined in a purely declarative manner without resorting to compile-time programming. The
macros are thus terminating in that parsing is guaranteed to
terminate, hygienic since full 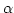 -conversion eliminates the
risk of name clashes, and transparent such that subsequent phases in
the compiler are unaware of them. Error messages from later phases in the
compiler are tracked through all macro invocations to pinpoint their sources
in the extended syntax. -conversion eliminates the
risk of name clashes, and transparent such that subsequent phases in
the compiler are unaware of them. Error messages from later phases in the
compiler are tracked through all macro invocations to pinpoint their sources
in the extended syntax.
A concept of metamorphic rules allows
the arguments of a macro to be defined in an almost arbitrary meta
level grammar and then to be morphed into the host language.
We show through examples how creative use of metamorphic syntax macros may be
used not only to create convenient shorthand notation but also to introduce
new language concepts and mechanisms. In fact, whole new languages can be
created at surprisingly low cost. The resulting programs are significantly
easier to understand and maintain.
This work is fully implemented as
part of the  bigwig bigwig system for defining interactive Web services, but
could find use in many other languages. system for defining interactive Web services, but
could find use in many other languages.
- RS-00-23
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Luca Aceto, Anna Ingólfsdóttir,
Mikkel Lykke Pedersen, and Jan Poulsen.
Characteristic Formulae for Timed Automata.
September 2000.
23 pp. Appears in RAIRO, Theoretical Informatics and
Applications 34(6), pp. 565-584.
Abstract: This paper offers characteristic formula
constructions in the real-time logic 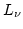 for several behavioural
relations between (states of) timed automata. The behavioural relations
studied in this work are timed (bi)similarity, timed ready simulation,
faster-than bisimilarity and timed trace inclusion. The characteristic
formulae delivered by our constructions have size which is linear in that of
the timed automaton they logically describe. This also applies to the
characteristic formula for timed bisimulation equivalence, for which an
exponential space construction was previously offered by Laroussinie, Larsen
and Weise. for several behavioural
relations between (states of) timed automata. The behavioural relations
studied in this work are timed (bi)similarity, timed ready simulation,
faster-than bisimilarity and timed trace inclusion. The characteristic
formulae delivered by our constructions have size which is linear in that of
the timed automaton they logically describe. This also applies to the
characteristic formula for timed bisimulation equivalence, for which an
exponential space construction was previously offered by Laroussinie, Larsen
and Weise.
- RS-00-22
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Thomas S. Hune and Anders B. Sandholm.
Using Automata in Control Synthesis -- A Case Study.
September 2000.
20 pp. Appears in Maibaum, editor, Fundamental Approaches to
Software Engineering: Third International Conference, FASE '00
Proceedings, LNCS 1783, 2000, pages 349-362.
Abstract: We study a method for synthesizing control programs.
The method merges an existing control program with a control automaton. For
specifying the control automata we have used monadic second order logic over
strings. Using the Mona tool, specifications are translated into automata.
This yields a new control program restricting the behavior of the old control
program such that the specifications are satisfied. The method is presented
through a concrete example.
- RS-00-21
-
PostScript,
PDF.
M. Oliver Möller and Rajeev Alur.
Heuristics for Hierarchical Partitioning with Application to
Model Checking.
August 2000.
30 pp. A shorter version appears in Margaria and Melham, editors,
Correct Hardware Design and Verification Methods, 11th IFIP WG 10.5
Advanced Research Working Conference, CHARME '01 Proceedings, LNCS 2144,
2001, pages 71-85.
Abstract: Given a collection of connected components, it is
often desired to cluster together parts of strong correspondence, yielding a
hierarchical structure. We address the automation of this process and apply
heuristics to battle the combinatorial and computational complexity. We
define a cost function that captures the quality of a structure relative to
the connections and favors shallow structures with a low degree of branching.
Finding a structure with minimal cost is shown to be 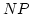 -complete. We
present a greedy polynomial-time algorithm that creates an approximative good
solution incrementally by local evaluation of a heuristic function. We
compare some simple heuristic functions and argue for one based on four
criteria: The number of enclosed connections, the number of components, the
number of touched connections and the depth of the structure. We report on an
application in the context of formal verification, where our algorithm serves
as a preprocessor for a temporal scaling technique, called ``Next''
heuristic. The latter is applicable in enumerative reachability analysis and
is included in the recent version of the MOCHA model checking tool. We
demonstrate performance and benefits of our method and use an asynchronous
parity computer, a standard leader election algorithm, and an opinion poll
protocol as case studies. -complete. We
present a greedy polynomial-time algorithm that creates an approximative good
solution incrementally by local evaluation of a heuristic function. We
compare some simple heuristic functions and argue for one based on four
criteria: The number of enclosed connections, the number of components, the
number of touched connections and the depth of the structure. We report on an
application in the context of formal verification, where our algorithm serves
as a preprocessor for a temporal scaling technique, called ``Next''
heuristic. The latter is applicable in enumerative reachability analysis and
is included in the recent version of the MOCHA model checking tool. We
demonstrate performance and benefits of our method and use an asynchronous
parity computer, a standard leader election algorithm, and an opinion poll
protocol as case studies.
- RS-00-20
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Luca Aceto, Willem Jan Fokkink, and Anna
Ingólfsdóttir.
2-Nested Simulation is not Finitely Equationally Axiomatizable.
August 2000.
13 pp. Appears in Ferreira and Reichel, editors, 18th Annual
Symposium on Theoretical Aspects of Computer Science, STACS '01
Proceedings, LNCS 2010, 2001, pages 39-50.
Abstract: 2-nested simulation was introduced by Groote and
Vaandrager as the coarsest equivalence included in completed trace
equivalence for which the tyft/tyxt format is a congruence format. In the
linear time-branching time spectrum of van Glabbeek, 2-nested simulation is
one of the few equivalences for which no finite equational axiomatization is
presented. In this paper we prove that such an axiomatization does not exist
for 2-nested simulation.
- RS-00-19
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Vinodchandran N. Variyam.
A Note on
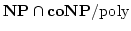 . .
August 2000.
7 pp.
Abstract: In this note we show that
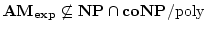 , where , where
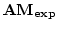 denotes the exponential version of the class denotes the exponential version of the class 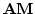 . The main part
of the proof is a collapse of . The main part
of the proof is a collapse of 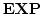 to to 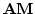 under the assumption
that under the assumption
that
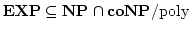 . .
- RS-00-18
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Federico Crazzolara and Glynn Winskel.
Language, Semantics, and Methods for Cryptographic Protocols.
August 2000.
ii+42 pp.
Abstract: In this report we present a process language for
security protocols together with an operational semantics and an alternative
semantics in terms of sets of events. The denotation of process is a set of
events, and as each event specifies a set of pre and postconditions, this
denotation can be viewed as a Petri net. This Petri-net semantics has a
strong relation to both Paulson's inductive set of rules and the strand space
approach. By means of an example we illustrate how the Petri-net semantics
can be used to prove properties such as secrecy and authentication.
- RS-00-17
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Thomas S. Hune.
Modeling a Language for Embedded Systems in Timed Automata.
August 2000.
26 pp. Earlier version entitled Modelling a Real-Time Language
appeared in Gnesi and Latella, editors, Fourth International ERCIM
Workshop on Formal Methods for Industrial Critical Systems, FMICS '99
Proceedings of the FLoC Workshop, 1999, pages 259-282.
Abstract: We present a compositional method for translating
real-time programs into networks of timed automata. Programs are written in
an assembly like real-time language and translated into models supported by
the tool Uppaal. We have implemented the translation and give an example of
its application on a simple control program for a car. Some properties of the
behavior of the control program are verified using the generated model.
- RS-00-16
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Jirí Srba.
Complexity of Weak Bisimilarity and Regularity for BPA and
BPP.
June 2000.
20 pp. To appear in Aceto and Victor, editors, Expressiveness in
Concurrency: 7th International Workshop, EXPRESS '00 Proceedings,
ENTCS 39(1), 2000.
Abstract: It is an open problem whether weak bisimilarity is
decidable for Basic Process Algebra (BPA) and Basic Parallel Processes (BPP).
A PSPACE lower bound for BPA and NP lower bound for BPP have been
demonstrated by Stribrna. Mayr achieved recently a result, saying that weak
bisimilarity for BPP is 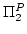 -hard. We improve this lower bound to
PSPACE, moreover for the restricted class of normed BPP. -hard. We improve this lower bound to
PSPACE, moreover for the restricted class of normed BPP.
Weak
regularity (finiteness) of BPA and BPP is not known to be decidable either.
In the case of BPP there is a 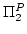 -hardness result by Mayr, which we
improve to PSPACE. No lower bound has previously been established for BPA. We
demonstrate DP-hardness, which in particular implies both NP and
co-NP-hardness. -hardness result by Mayr, which we
improve to PSPACE. No lower bound has previously been established for BPA. We
demonstrate DP-hardness, which in particular implies both NP and
co-NP-hardness.
In each of the bisimulation/regularity problems we
consider also the classes of normed processes.
- RS-00-15
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Daniel Damian and Olivier Danvy.
Syntactic Accidents in Program Analysis: On the Impact of the
CPS Transformation.
June 2000.
26 pp. Extended version of an article appearing in Wadler, editor,
Proceedings of the fifth ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on
Functional Programming, 2000, pages 209-220. To appear in Journal of
Functional Programming.
Abstract: We show that a non-duplicating CPS transformation has
no effect on control-flow analysis and that it has a positive effect on
binding-time analysis: a monovariant control-flow analysis yields strictly
comparable results on a direct-style program and on its CPS counterpart; and
a monovariant binding-time analysis yields more precise results on a CPS
program than on its direct-style counterpart. Our proof technique amounts to
constructing the continuation-passing style (CPS) counterpart of flow
information and of binding times.
Our results confirm a common
intuition about control-flow analysis, namely that it is orthogonal to the
CPS transformation. They also prove a folklore theorem about binding-time
analysis, namely that CPS has a positive impact on binding times. What may be
more surprising is that this beneficial effect holds even if contexts or
continuations are not duplicated.
The present study is symptomatic of
an unsettling property of program analyses: their quality is unpredictably
vulnerable to syntactic accidents in source programs, i.e., to the way these
programs are written. More reliable program analyses require a better
understanding of the effects of syntactic change.
- RS-00-14
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ronald Cramer, Ivan B. Damgård, and
Jesper Buus Nielsen.
Multiparty Computation from Threshold Homomorphic Encryption.
June 2000.
ii+38 pp. Appears in Pfitzmann, editor, Advances in Cryptology:
International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic
Techniques, EUROCRYPT '01 Proceedings, LNCS 2045, 2001, pages 280-300.
Abstract: We introduce a new approach to multiparty computation
(MPC) basing it on homomorphic threshold crypto-systems. We show that given
keys for any sufficiently efficient system of this type, general MPC
protocols for 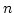 players can be devised which are secure against an active
adversary that corrupts any minority of the players. The total number of bits
sent is players can be devised which are secure against an active
adversary that corrupts any minority of the players. The total number of bits
sent is 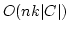 , where , where 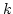 is the security parameter and is the security parameter and 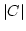 is the size
of a (Boolean) circuit computing the function to be securely evaluated. An
earlier proposal by Franklin and Haber with the same complexity was only
secure for passive adversaries, while all earlier protocols with active
security had complexity at least quadratic in is the size
of a (Boolean) circuit computing the function to be securely evaluated. An
earlier proposal by Franklin and Haber with the same complexity was only
secure for passive adversaries, while all earlier protocols with active
security had complexity at least quadratic in 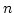 . We give two examples of
threshold cryptosystems that can support our construction and lead to the
claimed complexities. . We give two examples of
threshold cryptosystems that can support our construction and lead to the
claimed complexities.
- RS-00-13
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ondrej Klíma and Jirí
Srba.
Matching Modulo Associativity and Idempotency is NP-Complete.
June 2000.
19 pp. Appeared in Nielsen and Rovan, editors, Mathematical
Foundations of Computer Science: 25th International Symposium, MFCS '00
Proceedings, LNCS 1893, 2000, pages 456-466.
Abstract: We show that AI-matching (AI denotes the theory of an
associative and idempotent function symbol), which is solving matching word
equations in free idempotent semigroups, is NP-complete.
- RS-00-12
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Kohlenbach.
Intuitionistic Choice and Restricted Classical Logic.
May 2000.
9 pp. Appears in Mathematical Logic Quaterly vol 47, pp.
455-460, 2001,.
Abstract: Recently, Coquand and Palmgren considered systems of
intuitionistic arithmetic in all finite types together with various forms of
the axiom of choice and a numerical omniscience schema (NOS) which
implies classical logic for arithmetical formulas. Feferman subsequently
observed that the proof theoretic strength of such systems can be determined
by functional interpretation based on a non-constructive  -operator and
his well-known results on the strength of this operator from the 70's. -operator and
his well-known results on the strength of this operator from the 70's.
In
this note we consider a weaker form LNOS (lesser numerical omniscience
schema) of NOS which suffices to derive the strong form of binary
König's lemma studied by Coquand/Palmgren and gives rise to a new and
mathematically strong semi-classical system which, nevertheless, can proof
theoretically be reduced to primitive recursive arithmetic PRA. The
proof of this fact relies on functional interpretation and a majorization
technique developed in a previous paper.
- RS-00-11
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Jakob Pagter.
On Ajtai's Lower Bound Technique for 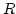 -way Branching
Programs and the Hamming Distance Problem. -way Branching
Programs and the Hamming Distance Problem.
May 2000.
18 pp.
Abstract: In this report we study the proof employed by Miklos
Ajtai [Determinism versus Non-Determinism for Linear Time RAMs with
Memory Restrictions, 31st Symposium on Theory of Computation (STOC), 1999]
when proving a non-trivial lower bound in a general model of computation for
the Hamming distance problem: given 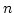 elements decide whether any two of
them have ``small'' Hamming distance. Specifically, Ajtai was able to show
that any elements decide whether any two of
them have ``small'' Hamming distance. Specifically, Ajtai was able to show
that any 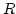 -way branching program deciding this problem using time -way branching program deciding this problem using time 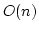 must use space
must use space
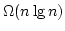 . We generalize Ajtai's original proof
allowing us to prove a time-space trade-off for deciding the Hamming distance
problem in the . We generalize Ajtai's original proof
allowing us to prove a time-space trade-off for deciding the Hamming distance
problem in the 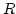 -way branching program model for time between -way branching program model for time between 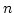 and and
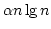 , for some suitable , for some suitable 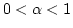 . In particular we prove that
if space is . In particular we prove that
if space is
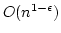 , then time is , then time is
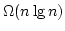 . .
- RS-00-10
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Stefan Dantchev and Søren Riis.
A Tough Nut for Tree Resolution.
May 2000.
13 pp.
Abstract: One of the earliest proposed hard problems for
theorem provers is a propositional version of the Mutilated Chessboard
problem. It is well known from recreational mathematics: Given a
chessboard having two diagonally opposite squares removed, prove that it
cannot be covered with dominoes. In Proof Complexity, we consider not
ordinary, but 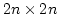 mutilated chessboard. In the paper, we show a mutilated chessboard. In the paper, we show a
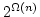 lower bound for tree resolution. lower bound for tree resolution.
- RS-00-9
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Kohlenbach.
Effective Uniform Bounds on the Krasnoselski-Mann
Iteration.
May 2000.
34 pp. The material of this report appeared as two publications: 1) A
Quantitative version of a theorem due to Borwein-Reich-Shafrir, Numer.Funct.
Aanal.Optimiz. 22, pp. 641-656 (2001), 2) On the computational content of the
Krasnoselski and Ishikawa fixed point theorems. In Blanck (et.al.) eds., CCA
2000, LNCS 2064, pp. 119-145 (2001).
Abstract: This paper is a case study in proof mining applied to
non-effective proofs in nonlinear functional anlysis. More specifically, we
are concerned with the fixed point theory of nonexpansive selfmappings 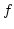 of
convex sets of
convex sets 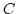 in normed spaces. We study the Krasnoselski iteration as well
as more general so-called Krasnoselski-Mann iterations. These iterations
converge to fixed points of in normed spaces. We study the Krasnoselski iteration as well
as more general so-called Krasnoselski-Mann iterations. These iterations
converge to fixed points of 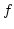 only under special compactness conditions and
even for uniformly convex spaces the rate of convergence is in general not
computable in only under special compactness conditions and
even for uniformly convex spaces the rate of convergence is in general not
computable in 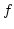 (which is related to the non-uniqueness of fixed points).
However, the iterations yield approximate fixed points of arbitrary quality
for general normed spaces and bounded (which is related to the non-uniqueness of fixed points).
However, the iterations yield approximate fixed points of arbitrary quality
for general normed spaces and bounded 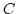 (asymptotic regularity). (asymptotic regularity).
In
this paper we apply general proof theoretic results obtained in previous
papers to non-effective proofs of this regularity and extract uniform
explicit bounds on the rate of the asymptotic regularity. We start off with
the classical case of uniformly convex spaces treated already by Krasnoselski
and show how a logically motivated modification allows to obtain an improved
bound. Already the analysis of the original proof (from 1955) yields an
elementary proof for a result which was obtained only in 1990 with the use of
the deep Browder-Göhde-Kirk fixed point theorem. The improved bound from
the modified proof gives applied to various special spaces results which
previously had been obtained only by ad hoc calculations and which in some
case are known to be optimal.
The main section of the paper deals with
the general case of arbitrary normed spaces and yields new results including
a quantitative analysis of a theorem due to Borwein, Reich and Shafrir (1992)
on the asymptotic behaviour of the general Krasnoselski-Mann iteration in
arbitrary normed spaces even for unbounded sets 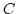 . Besides providing
explicit bounds we also get new qualitative results concerning the
independence of the rate of convergence of the norm of that iteration from
various input data. In the special case of bounded convex sets, where by
well-known results of Ishikawa, Edelstein/O'Brian and Goebel/Kirk the norm of
the iteration converges to zero, we obtain uniform bounds which do not depend
on the starting point of the iteration and the nonexpansive function and the
normed space . Besides providing
explicit bounds we also get new qualitative results concerning the
independence of the rate of convergence of the norm of that iteration from
various input data. In the special case of bounded convex sets, where by
well-known results of Ishikawa, Edelstein/O'Brian and Goebel/Kirk the norm of
the iteration converges to zero, we obtain uniform bounds which do not depend
on the starting point of the iteration and the nonexpansive function and the
normed space 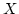 and, in fact, only depend on the error and, in fact, only depend on the error 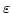 , an
upper bound on the diameter of , an
upper bound on the diameter of 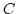 and some very general information on the
sequence of scalars and some very general information on the
sequence of scalars 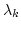 used in the iteration. Even non-effectively
only the existence of bounds satisfying weaker uniformity conditions was
known before except for the special situation, where used in the iteration. Even non-effectively
only the existence of bounds satisfying weaker uniformity conditions was
known before except for the special situation, where
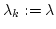 is
constant. For the unbounded case, no quantitative information was known so
far. is
constant. For the unbounded case, no quantitative information was known so
far.
- RS-00-8
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Nabil H. Mustafa and Aleksandar Pekec.
Democratic Consensus and the Local Majority Rule.
May 2000.
38 pp.
Abstract: In this paper we study a rather generic
communication/coordination/computation problem: in a finite network of
agents, each initially having one of the two possible states, can the
majority initial state be computed and agreed upon (i.e., can a democratic
consensus be reached) by means of iterative application of the local majority
rule. We show that this task is failure-free only in the networks that are
nowhere truly local. In other words, the idea of solving a truly global task
(reaching consensus on majority) by means of truly local computation only
(local majority rule) is doomed for failure.
We also show that even
well connected networks of agents that are nowhere truly local might fail to
reach democratic consensus when the local majority rule is applied
iteratively. Structural properties of democratic consensus computers, i.e.,
the networks in which iterative application of the local majority rule always
yields consensus in the initial majority state, are presented.
- RS-00-7
-
Lars Arge and Jakob Pagter.
I/O-Space Trade-Offs.
April 2000.
Appears in Halldórsson, editor, 7th Scandinavian Workshop on
Algorithm Theory, SWAT '98 Proceedings, LNCS 1851, 2000, pages 448-461.
Abstract: We define external memory (or I/O) models which
capture space complexity and develop a general technique for deriving
I/O-space trade-offs in these models from internal memory model time-space
trade-offs. Using this technique we show strong I/O-space product lower
bounds for Sorting and Element Distinctness. We also develop new space
efficient external memory Sorting algorithms.
- RS-00-6
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ivan B. Damgård and Jesper Buus
Nielsen.
Improved Non-Committing Encryption Schemes based on a General
Complexity Assumption.
March 2000.
24 pp. Appears in Bellare, editor, Advances in Cryptology: 20th
Annual International Cryptology Conference, CRYPTO '00 Proceedings,
LNCS 1880, 2000, pages 433-451.
Abstract: Non-committing encryption enables the construction of
multiparty computation protocols secure against an adaptive adversary
in the computational setting where private channels between players are not
assumed. While any non-committing encryption scheme must be secure in the
ordinary semantic sense, the converse is not necessarily true. We propose a
construction of non-committing encryption that can be based on any public key
system which is secure in the ordinary sense and which has an extra property
we call simulatability. The construction contains an earlier proposed
scheme by Beaver based on the Diffie-Hellman problem as a special case, and
we propose another implementation based on RSA. In a more general setting,
our construction can be based on any collection of trapdoor one-way
permutations with a certain simulatability property. This offers a
considerable efficiency improvement over the first non-committing encryption
scheme proposed by Canetti et al. Finally, at some loss of efficiency, our
scheme can be based on general collections of trapdoor one-way permutations
without the simulatability assumption, and without the common domain
assumption of Canetti et al.
- RS-00-5
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ivan B. Damgård and Mads J. Jurik.
Efficient Protocols based on Probabilistic Encryption using
Composite Degree Residue Classes.
March 2000.
19 pp.
Abstract: We study various applications and variants of
Paillier's probabilistic encryption scheme. First, we propose a threshold
variant of the scheme, and also zero-knowledge protocols for proving that a
given ciphertext encodes a given plaintext, and for verifying multiplication
of encrypted values.
We then show how these building blocks can be
used for applying the scheme to efficient electronic voting. This reduces
dramatically the work needed to compute the final result of an election,
compared to the previously best known schemes. We show how the basic scheme
for a yes/no vote can be easily adapted to casting a vote for up to 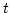 out
of out
of 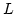 candidates. The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to
provide receipt-free elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The
scheme for 1 out of candidates. The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to
provide receipt-free elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The
scheme for 1 out of 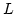 elections can be optimised such that for a certain
range of parameter values, a ballot has size only elections can be optimised such that for a certain
range of parameter values, a ballot has size only 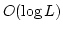 bits. bits.
Finally, we propose a variant of the encryption scheme, that allows reducing
the expansion factor of Paillier's scheme from 2 to almost 1.
- RS-00-4
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Rasmus Pagh.
A New Trade-off for Deterministic Dictionaries.
February 2000.
Appears in Halldórsson, editor, 7th Scandinavian Workshop on
Algorithm Theory, SWAT '98 Proceedings, LNCS 1851, 2000, pages 22-31.
Journal version in Nordic Journal of Computing 7(3):151-163, 2000 with
the title A Trade-Off for Worst-Case Efficient Dictionaries.
Abstract: We consider dictionaries over the universe
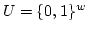 on a unit-cost RAM with word size on a unit-cost RAM with word size 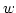 and a standard
instruction set. We present a linear space deterministic dictionary with
membership queries in time and a standard
instruction set. We present a linear space deterministic dictionary with
membership queries in time
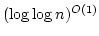 and updates in time and updates in time
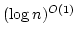 , where , where 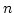 is the size of the set stored. This is the first such
data structure to simultaneously achieve query time is the size of the set stored. This is the first such
data structure to simultaneously achieve query time
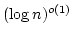 and
update time and
update time
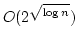 . .
- RS-00-3
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Fredrik Larsson, Paul Pettersson, and Wang
Yi.
On Memory-Block Traversal Problems in Model Checking Timed
Systems.
January 2000.
15 pp. Appears in Graf and Schwartzbach, editors, Tools and
Algorithms for The Construction and Analysis of Systems: 6th International
Conference, TACAS '00 Proceedings, LNCS 1785, 2000, pages 127-141.
Abstract: A major problem in model-checking timed systems is
the huge memory requirement. In this paper, we study the memory-block
traversal problems of using standard operating systems in exploring the
state-space of timed automata. We report a case study which demonstrates that
deallocating memory blocks (i.e. memory-block traversal) using standard
memory management routines is extremely time-consuming. The phenomenon is
demonstrated in a number of experiments by installing the UPPAAL tool on
Windows95, SunOS 5 and Linux. It seems that the problem should be solved by
implementing a memory manager for the model-checker, which is a troublesome
task as it is involved in the underlining hardware and operating system. We
present an alternative technique that allows the model-checker to control the
memory-block traversal strategies of the operating systems without
implementing an independent memory manager. The technique is implemented in
the UPPAAL model-checker. Our experiments demonstrate that it results in
significant improvement on the performance of UPPAAL. For example, it reduces
the memory deallocation time in checking a start-up synchronisation protocol
on Linux from 7 days to about 1 hour. We show that the technique can also be
applied in speeding up re-traversals of explored state-space.
- RS-00-2
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Igor Walukiewicz.
Local Logics for Traces.
January 2000.
30 pp. To appear in Journal of Automata, Languages and
Combinatorics.
Abstract: A mu-calculus over dependence graph representation of
traces is considered. It is shown that the mu-calculus cannot express all
monadic second order (MSO) properties of dependence graphs. Several
extensions of the mu-calculus are presented and it is proved that these
extensions are equivalent in expressive power to MSO logic. The
satisfiability problem for these extensions is PSPACE complete.
- RS-00-1
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Rune B. Lyngsø and Christian N. S.
Pedersen.
Pseudoknots in RNA Secondary Structures.
January 2000.
15 pp. Appears in Shamir, editor, Fourth Annual International
Conference on Computational Molecular Biology, RECOMB '00 Proceedings,
2000, 201-209 and in Journal of Computational Biology,
7(3/4):409-427, 2000.
Abstract: RNA molecules are sequences of nucleotides that serve
as more than mere intermediaries between DNA and proteins, e.g. as catalytic
molecules. Computational prediction of RNA secondary structure is among the
few structure prediction problems that can be solved satisfactory in
polynomial time. Most work has been done to predict structures that do not
contain pseudoknots. Allowing pseudoknots introduce modelling and
computational problems. In this paper we consider the problem of predicting
RNA secondary structure when certain types of pseudoknots are allowed. We
first present an algorithm that in time 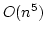 and space and space 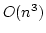 predicts
the secondary structure of an RNA sequence of length predicts
the secondary structure of an RNA sequence of length 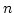 in a model that
allows certain kinds of pseudoknots. We then prove that the general problem
of predicting RNA secondary structure containing pseudoknots is NP-complete for a large class of reasonable models of pseudoknots. in a model that
allows certain kinds of pseudoknots. We then prove that the general problem
of predicting RNA secondary structure containing pseudoknots is NP-complete for a large class of reasonable models of pseudoknots.
|
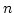 , the construction of the statistically concealing scheme
requires
, the construction of the statistically concealing scheme
requires 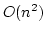 executions of the statistically binding scheme. As a
consequence, statistically concealing but computationally binding quantum bit
commitments can be based upon any family of quantum one-way functions. Such a
construction is not known to exist in the classical world.
executions of the statistically binding scheme. As a
consequence, statistically concealing but computationally binding quantum bit
commitments can be based upon any family of quantum one-way functions. Such a
construction is not known to exist in the classical world.
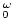 of the second order base system RCA
of the second order base system RCA . By this
conservation nothing is lost for second order statements if we reason in
RCA
. By this
conservation nothing is lost for second order statements if we reason in
RCA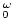 instead of RCA
instead of RCA . However, the presence of finite types
allows to treat various analytical notions in a rather direct way, compared
to the encodings needed in RCA
. However, the presence of finite types
allows to treat various analytical notions in a rather direct way, compared
to the encodings needed in RCA which are not always provably faithful in
RCA
which are not always provably faithful in
RCA . Moreover, the language of finite types allows to treat many more
principles and gives rise to interesting extensions of the existing scheme of
reverse mathematics. We indicate this by showing that the class of principles
equivalent (over RCA
. Moreover, the language of finite types allows to treat many more
principles and gives rise to interesting extensions of the existing scheme of
reverse mathematics. We indicate this by showing that the class of principles
equivalent (over RCA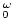 ) to Feferman's non-constructive
) to Feferman's non-constructive
 -operator forms a mathematically rich and very robust class. This is
closely related to a phenomenon in higher type recursion theory known as
Grilliot's trick.
-operator forms a mathematically rich and very robust class. This is
closely related to a phenomenon in higher type recursion theory known as
Grilliot's trick.
 -calculus.
Known strategy improvement algorithms, as proposed for stochastic games by
Hoffman and Karp in 1966, and for discounted payoff games and parity games by
Puri in 1995, work with real numbers and require solving linear programming
instances involving high precision arithmetic. In the present algorithm for
parity games these difficulties are avoided by the use of discrete vertex
valuations in which information about the relevance of vertices and certain
distances is coded. An efficient implementation is given for a strategy
improvement step. Another advantage of the present approach is that it
provides a better conceptual understanding and easier analysis of strategy
improvement algorithms for parity games. However, so far it is not known
whether the present algorithm works in polynomial time. The long standing
problem whether parity games can be solved in polynomial time remains open.
-calculus.
Known strategy improvement algorithms, as proposed for stochastic games by
Hoffman and Karp in 1966, and for discounted payoff games and parity games by
Puri in 1995, work with real numbers and require solving linear programming
instances involving high precision arithmetic. In the present algorithm for
parity games these difficulties are avoided by the use of discrete vertex
valuations in which information about the relevance of vertices and certain
distances is coded. An efficient implementation is given for a strategy
improvement step. Another advantage of the present approach is that it
provides a better conceptual understanding and easier analysis of strategy
improvement algorithms for parity games. However, so far it is not known
whether the present algorithm works in polynomial time. The long standing
problem whether parity games can be solved in polynomial time remains open.
 out of
out of  candidates.
The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to provide receipt-free
elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The scheme for 1 out of
candidates.
The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to provide receipt-free
elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The scheme for 1 out of
 elections can be optimised such that for a certain range of parameter
values, a ballot has size only
elections can be optimised such that for a certain range of parameter
values, a ballot has size only 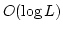 bits.
bits.
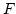 is dispersing if, for any set
is dispersing if, for any set
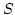 of a certain size and random
of a certain size and random 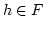 , the expected value of
, the expected value of ![$\vert S\vert-\vert h[S]\vert$](img12.gif) is not much larger than the expectancy if
is not much larger than the expectancy if 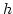 had been chosen at random from
the set of all functions.
had been chosen at random from
the set of all functions. -lattices.
-lattices.
 -term, that is a term built up using also a least fixed point
constructor as well as a greatest fixed point constructor, is equivalent to a
-term, that is a term built up using also a least fixed point
constructor as well as a greatest fixed point constructor, is equivalent to a
 -term where the number of nested fixed point of a different type is
bounded by a fixed number.
-term where the number of nested fixed point of a different type is
bounded by a fixed number. -lattices is strict, meaning
that such number does not exist if
-lattices is strict, meaning
that such number does not exist if  -terms are built up from the basic
lattice operations and are interpreted as expected. The proof relies on the
explicit characterization of free
-terms are built up from the basic
lattice operations and are interpreted as expected. The proof relies on the
explicit characterization of free  -lattices by means of games and
strategies.
-lattices by means of games and
strategies.
 -lattices.
-lattices.
 -lattice is a lattice with the property that
every unary polynomial has both a least and a greatest fix-point. In this
paper we define the quasivariety of
-lattice is a lattice with the property that
every unary polynomial has both a least and a greatest fix-point. In this
paper we define the quasivariety of  -lattices and, for a given partially
ordered set
-lattices and, for a given partially
ordered set 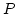 , we construct a
, we construct a  -lattice
-lattice 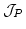 whose elements
are equivalence classes of games in a preordered class
whose elements
are equivalence classes of games in a preordered class 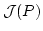 . We
prove that the
. We
prove that the  -lattice
-lattice  is free over the ordered set
is free over the ordered set  and that the order relation of
and that the order relation of
 is decidable if the order
relation of
is decidable if the order
relation of  is decidable. By means of this characterization of free
is decidable. By means of this characterization of free
 -lattices we infer that the class of complete lattices generates the
quasivariety of
-lattices we infer that the class of complete lattices generates the
quasivariety of  -lattices.
-lattices.
 -Semirings.
-Semirings.
 -semirings are partially ordered semirings equipped with
a star operation satisfying the fixed point equation and the fixed point
induction rule for linear terms. Inductive
-semirings are partially ordered semirings equipped with
a star operation satisfying the fixed point equation and the fixed point
induction rule for linear terms. Inductive  -semirings are extensions of
continuous semirings and the Kleene algebras of Conway and Kozen.
-semirings are extensions of
continuous semirings and the Kleene algebras of Conway and Kozen. -semirings in relation to automata, languages and power series. In
particular, we prove that if
-semirings in relation to automata, languages and power series. In
particular, we prove that if 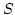 is an inductive
is an inductive  -semiring, then so is
the semiring of matrices
-semiring, then so is
the semiring of matrices
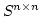 , for any integer
, for any integer 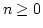 , and
that if
, and
that if 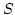 is an inductive
is an inductive  -semiring, then so is any semiring of power
series
-semiring, then so is any semiring of power
series
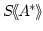 . As shown
by Kozen, the dual of an inductive
. As shown
by Kozen, the dual of an inductive  -semiring may not be inductive. In
contrast, we show that the dual of an iteration semiring is an iteration
semiring. Kuich proved a general Kleene theorem for continuous semirings, and
Bloom and Ésik proved a Kleene theorem for all Conway semirings. Since
any inductive
-semiring may not be inductive. In
contrast, we show that the dual of an iteration semiring is an iteration
semiring. Kuich proved a general Kleene theorem for continuous semirings, and
Bloom and Ésik proved a Kleene theorem for all Conway semirings. Since
any inductive  -semiring is a Conway semiring and an iteration semiring,
as we show, there results a Kleene theorem applicable to all inductive
-semiring is a Conway semiring and an iteration semiring,
as we show, there results a Kleene theorem applicable to all inductive
 -semirings. We also describe the structure of the initial inductive
-semirings. We also describe the structure of the initial inductive
 -semiring and conjecture that any free inductive
-semiring and conjecture that any free inductive  -semiring may be
given as a semiring of rational power series with coefficients in the initial
inductive
-semiring may be
given as a semiring of rational power series with coefficients in the initial
inductive  -semiring. We relate this conjecture to recent axiomatization
results on the equational theory of the regular sets.
-semiring. We relate this conjecture to recent axiomatization
results on the equational theory of the regular sets.
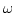 -)continuous functions on (
-)continuous functions on (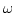 -)complete
partially ordered sets are captured by the axioms of (ordered) iteration
algebras, or iteration theories. We show that the inequational laws of the
sum operation in conjunction with the least fixed point operation in
continuous additive algebras have a finite axiomatization over the
inequations of ordered iteration algebras. As a byproduct of this relative
axiomatizability result, we obtain complete infinite inequational and finite
implicational axiomatizations. Along the way of proving these results, we
give a concrete description of the free algebras in the corresponding variety
of ordered iteration algebras. This description uses injective simulations of
regular synchronization trees. Thus, our axioms are also sound and complete
for the injective simulation (resource bounded simulation) of (regular)
processes.
-)complete
partially ordered sets are captured by the axioms of (ordered) iteration
algebras, or iteration theories. We show that the inequational laws of the
sum operation in conjunction with the least fixed point operation in
continuous additive algebras have a finite axiomatization over the
inequations of ordered iteration algebras. As a byproduct of this relative
axiomatizability result, we obtain complete infinite inequational and finite
implicational axiomatizations. Along the way of proving these results, we
give a concrete description of the free algebras in the corresponding variety
of ordered iteration algebras. This description uses injective simulations of
regular synchronization trees. Thus, our axioms are also sound and complete
for the injective simulation (resource bounded simulation) of (regular)
processes.
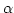 -conversion eliminates the
risk of name clashes, and transparent such that subsequent phases in
the compiler are unaware of them. Error messages from later phases in the
compiler are tracked through all macro invocations to pinpoint their sources
in the extended syntax.
-conversion eliminates the
risk of name clashes, and transparent such that subsequent phases in
the compiler are unaware of them. Error messages from later phases in the
compiler are tracked through all macro invocations to pinpoint their sources
in the extended syntax. bigwig
bigwig system for defining interactive Web services, but
could find use in many other languages.
system for defining interactive Web services, but
could find use in many other languages.
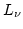 for several behavioural
relations between (states of) timed automata. The behavioural relations
studied in this work are timed (bi)similarity, timed ready simulation,
faster-than bisimilarity and timed trace inclusion. The characteristic
formulae delivered by our constructions have size which is linear in that of
the timed automaton they logically describe. This also applies to the
characteristic formula for timed bisimulation equivalence, for which an
exponential space construction was previously offered by Laroussinie, Larsen
and Weise.
for several behavioural
relations between (states of) timed automata. The behavioural relations
studied in this work are timed (bi)similarity, timed ready simulation,
faster-than bisimilarity and timed trace inclusion. The characteristic
formulae delivered by our constructions have size which is linear in that of
the timed automaton they logically describe. This also applies to the
characteristic formula for timed bisimulation equivalence, for which an
exponential space construction was previously offered by Laroussinie, Larsen
and Weise.
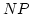 -complete. We
present a greedy polynomial-time algorithm that creates an approximative good
solution incrementally by local evaluation of a heuristic function. We
compare some simple heuristic functions and argue for one based on four
criteria: The number of enclosed connections, the number of components, the
number of touched connections and the depth of the structure. We report on an
application in the context of formal verification, where our algorithm serves
as a preprocessor for a temporal scaling technique, called ``Next''
heuristic. The latter is applicable in enumerative reachability analysis and
is included in the recent version of the MOCHA model checking tool. We
demonstrate performance and benefits of our method and use an asynchronous
parity computer, a standard leader election algorithm, and an opinion poll
protocol as case studies.
-complete. We
present a greedy polynomial-time algorithm that creates an approximative good
solution incrementally by local evaluation of a heuristic function. We
compare some simple heuristic functions and argue for one based on four
criteria: The number of enclosed connections, the number of components, the
number of touched connections and the depth of the structure. We report on an
application in the context of formal verification, where our algorithm serves
as a preprocessor for a temporal scaling technique, called ``Next''
heuristic. The latter is applicable in enumerative reachability analysis and
is included in the recent version of the MOCHA model checking tool. We
demonstrate performance and benefits of our method and use an asynchronous
parity computer, a standard leader election algorithm, and an opinion poll
protocol as case studies.
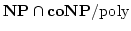 .
.
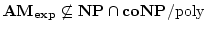 , where
, where
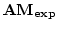 denotes the exponential version of the class
denotes the exponential version of the class 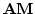 . The main part
of the proof is a collapse of
. The main part
of the proof is a collapse of 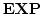 to
to 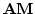 under the assumption
that
under the assumption
that
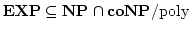 .
.
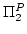 -hard. We improve this lower bound to
PSPACE, moreover for the restricted class of normed BPP.
-hard. We improve this lower bound to
PSPACE, moreover for the restricted class of normed BPP.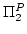 -hardness result by Mayr, which we
improve to PSPACE. No lower bound has previously been established for BPA. We
demonstrate DP-hardness, which in particular implies both NP and
co-NP-hardness.
-hardness result by Mayr, which we
improve to PSPACE. No lower bound has previously been established for BPA. We
demonstrate DP-hardness, which in particular implies both NP and
co-NP-hardness.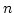 players can be devised which are secure against an active
adversary that corrupts any minority of the players. The total number of bits
sent is
players can be devised which are secure against an active
adversary that corrupts any minority of the players. The total number of bits
sent is 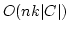 , where
, where 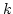 is the security parameter and
is the security parameter and 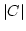 is the size
of a (Boolean) circuit computing the function to be securely evaluated. An
earlier proposal by Franklin and Haber with the same complexity was only
secure for passive adversaries, while all earlier protocols with active
security had complexity at least quadratic in
is the size
of a (Boolean) circuit computing the function to be securely evaluated. An
earlier proposal by Franklin and Haber with the same complexity was only
secure for passive adversaries, while all earlier protocols with active
security had complexity at least quadratic in 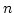 . We give two examples of
threshold cryptosystems that can support our construction and lead to the
claimed complexities.
. We give two examples of
threshold cryptosystems that can support our construction and lead to the
claimed complexities.
 -operator and
his well-known results on the strength of this operator from the 70's.
-operator and
his well-known results on the strength of this operator from the 70's.
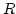 -way Branching
Programs and the Hamming Distance Problem.
-way Branching
Programs and the Hamming Distance Problem.
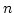 elements decide whether any two of
them have ``small'' Hamming distance. Specifically, Ajtai was able to show
that any
elements decide whether any two of
them have ``small'' Hamming distance. Specifically, Ajtai was able to show
that any 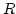 -way branching program deciding this problem using time
-way branching program deciding this problem using time  must use space
must use space
 . We generalize Ajtai's original proof
allowing us to prove a time-space trade-off for deciding the Hamming distance
problem in the
. We generalize Ajtai's original proof
allowing us to prove a time-space trade-off for deciding the Hamming distance
problem in the  -way branching program model for time between
-way branching program model for time between 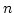 and
and
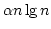 , for some suitable
, for some suitable 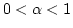 . In particular we prove that
if space is
. In particular we prove that
if space is
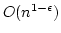 , then time is
, then time is
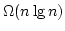 .
.
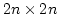 mutilated chessboard. In the paper, we show a
mutilated chessboard. In the paper, we show a
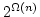 lower bound for tree resolution.
lower bound for tree resolution.
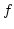 of
convex sets
of
convex sets 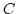 in normed spaces. We study the Krasnoselski iteration as well
as more general so-called Krasnoselski-Mann iterations. These iterations
converge to fixed points of
in normed spaces. We study the Krasnoselski iteration as well
as more general so-called Krasnoselski-Mann iterations. These iterations
converge to fixed points of 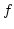 only under special compactness conditions and
even for uniformly convex spaces the rate of convergence is in general not
computable in
only under special compactness conditions and
even for uniformly convex spaces the rate of convergence is in general not
computable in 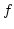 (which is related to the non-uniqueness of fixed points).
However, the iterations yield approximate fixed points of arbitrary quality
for general normed spaces and bounded
(which is related to the non-uniqueness of fixed points).
However, the iterations yield approximate fixed points of arbitrary quality
for general normed spaces and bounded 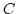 (asymptotic regularity).
(asymptotic regularity).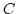 . Besides providing
explicit bounds we also get new qualitative results concerning the
independence of the rate of convergence of the norm of that iteration from
various input data. In the special case of bounded convex sets, where by
well-known results of Ishikawa, Edelstein/O'Brian and Goebel/Kirk the norm of
the iteration converges to zero, we obtain uniform bounds which do not depend
on the starting point of the iteration and the nonexpansive function and the
normed space
. Besides providing
explicit bounds we also get new qualitative results concerning the
independence of the rate of convergence of the norm of that iteration from
various input data. In the special case of bounded convex sets, where by
well-known results of Ishikawa, Edelstein/O'Brian and Goebel/Kirk the norm of
the iteration converges to zero, we obtain uniform bounds which do not depend
on the starting point of the iteration and the nonexpansive function and the
normed space 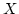 and, in fact, only depend on the error
and, in fact, only depend on the error 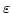 , an
upper bound on the diameter of
, an
upper bound on the diameter of 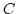 and some very general information on the
sequence of scalars
and some very general information on the
sequence of scalars 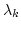 used in the iteration. Even non-effectively
only the existence of bounds satisfying weaker uniformity conditions was
known before except for the special situation, where
used in the iteration. Even non-effectively
only the existence of bounds satisfying weaker uniformity conditions was
known before except for the special situation, where
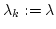 is
constant. For the unbounded case, no quantitative information was known so
far.
is
constant. For the unbounded case, no quantitative information was known so
far.
 out
of
out
of  candidates. The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to
provide receipt-free elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The
scheme for 1 out of
candidates. The same basic building blocks can also be adapted to
provide receipt-free elections, under appropriate physical assumptions. The
scheme for 1 out of 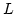 elections can be optimised such that for a certain
range of parameter values, a ballot has size only
elections can be optimised such that for a certain
range of parameter values, a ballot has size only 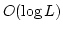 bits.
bits. on a unit-cost RAM with word size
on a unit-cost RAM with word size 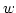 and a standard
instruction set. We present a linear space deterministic dictionary with
membership queries in time
and a standard
instruction set. We present a linear space deterministic dictionary with
membership queries in time
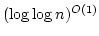 and updates in time
and updates in time
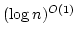 , where
, where  is the size of the set stored. This is the first such
data structure to simultaneously achieve query time
is the size of the set stored. This is the first such
data structure to simultaneously achieve query time
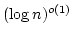 and
update time
and
update time
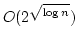 .
.
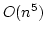 and space
and space  predicts
the secondary structure of an RNA sequence of length
predicts
the secondary structure of an RNA sequence of length  in a model that
allows certain kinds of pseudoknots. We then prove that the general problem
of predicting RNA secondary structure containing pseudoknots is NP-complete for a large class of reasonable models of pseudoknots.
in a model that
allows certain kinds of pseudoknots. We then prove that the general problem
of predicting RNA secondary structure containing pseudoknots is NP-complete for a large class of reasonable models of pseudoknots.