This document is also available as
PostScript
and
DVI.
- RS-02-53
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy.
A Lambda-Revelation of the SECD Machine.
December 2003.
15 pp. Superseeded by the BRICS report
RS-03-33.
Abstract: We present a simple inter-derivation between
lambda-interpreters, i.e., evaluation functions for lambda-terms, and
abstract reduction machines for the lambda-calculus, i.e., transition
functions. The two key derivation steps are the CPS transformation and
Reynolds's defunctionalization. By transforming the interpreter into
continuation-passing style (CPS), its flow of control is made manifest as a
continuation. By defunctionalizing this continuation, the flow of control is
materialized as a first-order data structure.
The derivation applies
not merely to connect independently known lambda-interpreters and abstract
machines, it also applies to construct the abstract machine corresponding to
a lambda-interpreter and to construct the lambda-interpreter corresponding to
an abstract machine. In this article, we treat in detail the canonical
example of Landin's SECD machine and we reveal its denotational content: the
meaning of an expression is a partial endo-function from a stack of
intermediate results and an environment to a new stack of intermediate
results and an environment. The corresponding lambda-interpreter is
unconventional because (1) it uses a control delimiter to evaluate the body
of each lambda-abstraction and (2) it assumes the environment to be managed
in a callee-save fashion instead of in the usual caller-save fashion.
- RS-02-52
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy.
A New One-Pass Transformation into Monadic Normal Form.
December 2002.
16 pp. Appears in Hedin, editor, Compiler Construction, 12th
International Conference, CC '03 Proceedings, LNCS 2622, 2003, pages
77-89.
Abstract: We present a translation from the call-by-value
lambda-calculus to monadic normal forms that includes short-cut boolean
evaluation. The translation is higher-order, operates in one pass, duplicates
no code, generates no chains of thunks, and is properly tail recursive. It
makes a crucial use of symbolic computation at translation time.
- RS-02-51
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Gerth Stølting Brodal, Rolf Fagerberg,
Anna Östlin, Christian N. S. Pedersen, and S. Srinivasa Rao.
Computing Refined Buneman Trees in Cubic Time.
December 2002.
14 pp. Appears in Benson and Page, editors, Algorithms in
Bioinformatics: 2nd International Workshop, WABI '03 Proceedings,
LNCS 2812, 2003, pages 259-270.
Abstract: Reconstructing the evolutionary tree for a set of
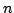 species based on pairwise distances between the species is a fundamental
problem in bioinformatics. Neighbor joining is a popular distance based tree
reconstruction method. It always proposes fully resolved binary trees despite
missing evidence in the underlying distance data. Distance based methods
based on the theory of Buneman trees and refined Buneman trees avoid this
problem by only proposing evolutionary trees whose edges satisfy a number of
constraints. These trees might not be fully resolved but there is strong
combinatorial evidence for each proposed edge. The currently best algorithm
for computing the refined Buneman tree from a given distance measure has a
running time of species based on pairwise distances between the species is a fundamental
problem in bioinformatics. Neighbor joining is a popular distance based tree
reconstruction method. It always proposes fully resolved binary trees despite
missing evidence in the underlying distance data. Distance based methods
based on the theory of Buneman trees and refined Buneman trees avoid this
problem by only proposing evolutionary trees whose edges satisfy a number of
constraints. These trees might not be fully resolved but there is strong
combinatorial evidence for each proposed edge. The currently best algorithm
for computing the refined Buneman tree from a given distance measure has a
running time of 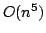 and a space consumption of and a space consumption of 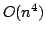 . In this paper,
we present an algorithm with running time . In this paper,
we present an algorithm with running time 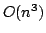 and space
consumption and space
consumption 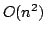 . .
- RS-02-50
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Kristoffer Arnsfelt Hansen, Peter Bro
Miltersen, and V. Vinay.
Circuits on Cylinders.
December 2002.
16 pp.
Abstract: We consider the computational power of constant width
polynomial size cylindrical circuits and nondeterministic branching programs.
We show that every function computed by a
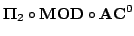 circuit can also be computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical nondeterministic branching program (or
cylindrical circuit) and that every function computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical circuit belongs to circuit can also be computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical nondeterministic branching program (or
cylindrical circuit) and that every function computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical circuit belongs to
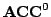 . .
- RS-02-49
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Mikkel Nygaard and Glynn Winskel.
HOPLA--A Higher-Order Process Language.
December 2002.
18 pp. Appears in Brim, Jancar, Kretínský and
Antonín, editors, Concurrency Theory: 13th International
Conference, CONCUR '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2421, 2002, pages 434-448.
Abstract: A small but powerful language for higher-order
nondeterministic processes is introduced. Its roots in a linear domain theory
for concurrency are sketched though for the most part it lends itself to a
more operational account. The language can be viewed as an extension of the
lambda calculus with a ``prefixed sum'', in which types express the form of
computation path of which a process is capable. Its operational semantics,
bisimulation, congruence properties and expressive power are explored; in
particular, it is shown how it can directly encode process languages such as
CCS, CCS with process passing, and mobile ambients with public names.
- RS-02-48
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Mikkel Nygaard and Glynn Winskel.
Linearity in Process Languages.
December 2002.
27 pp. Appears in Plotkin, editor, Seventeenth Annual IEEE
Symposium on Logic in Computer Science, Lics '02 Proceedings, 2002, pages
433-446.
Abstract: The meaning and mathematical consequences of
linearity (managing without a presumed ability to copy) are studied for a
path-based model of processes which is also a model of affine-linear logic.
This connection yields an affine-linear language for processes,
automatically respecting open-map bisimulation, in which a range of process
operations can be expressed. An operational semantics is provided for the
tensor fragment of the language. Different ways to make assemblies of
processes lead to different choices of exponential, some of which respect
bisimulation.
- RS-02-47
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Zoltán Ésik.
Extended Temporal Logic on Finite Words and Wreath Product of
Monoids with Distinguished Generators.
December 2002.
16 pp. Appears in Ito and Toyama, editors, 6th International
Conference, Developments in Language Theory, DLT '02 Revised Papers,
LNCS 2450, 2003, pages 43-48.
Abstract: We associate a modal operator with each language
belonging to a given class of regular languages and use the (reverse) wreath
product of monoids with distinguished generators to characterize the
expressive power of the resulting logic.
- RS-02-46
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Zoltán Ésik and Hans Leiß.
Greibach Normal Form in Algebraically Complete Semirings.
December 2002.
43 pp. An extended abstract appears in Bradfield, editor, European Association for Computer Science Logic: 16th International
Workshop, CSL '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2471, 2002, pages 135-150.
Abstract: We give inequational and equational axioms for
semirings with a fixed-point operator and formally develop a fragment of the
theory of context-free languages. In particular, we show that Greibach's
normal form theorem depends only on a few equational properties of least
pre-fixed-points in semirings, and elimination of chain- and deletion rules
depend on their inequational properties (and the idempotency of addition). It
follows that these normal form theorems also hold in non-continuous semirings
having enough fixed-points.
- RS-02-45
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Jesper Makholm Byskov.
Chromatic Number in Time 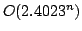 Using Maximal Independent
Sets. Using Maximal Independent
Sets.
December 2002.
6 pp.
Abstract: In this paper we improve an algorithm by Eppstein
(2001) for finding the chromatic number of a graph. We modify the algorithm
slightly, and by using a bound on the number of maximal independent sets of
size 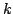 from our recent paper (2003), we prove that the running time is from our recent paper (2003), we prove that the running time is
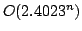 . Eppstein's algorithm runs in time . Eppstein's algorithm runs in time 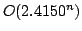 . The space
usage for both algorithms is . The space
usage for both algorithms is 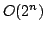 . .
- RS-02-44
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Zoltán Ésik and Zoltán L.
Németh.
Higher Dimensional Automata.
November 2002.
32 pp. A preliminary version appears under the title Automata on
Series-Parallel Biposets in Kuich, Rozenberg and Salomaa, editors, 5th International Conference, Developments in Language Theory, DLT '01
Revised Papers, LNCS 2295, 2002, pages 217-227. This report supersedes the
earlier BRICS report RS-01-24.
Abstract: We provide the basics of a 2-dimensional theory of
automata on series-parallel biposets. We define recognizable, regular and
rational sets of series-parallel biposets and study their relationship.
Moreover, we relate these classes to languages of series-parallel biposets
definable in monadic second-order logic.
- RS-02-43
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Mikkel Christiansen and Emmanuel Fleury.
Using IDDs for Packet Filtering.
October 2002.
25 pp.
Abstract: Firewalls are one of the key technologies used to
control the traffic going in and out of a network. A central feature of the
firewall is the packet filter. In this paper, we propose a complete
framework for packet classification. Through two applications we demonstrate
that both performance and security can be improved.
We show that a
traditional ordered rule set can always be expressed as a first-order logic
formula on integer variables. Moreover, we emphasize that, with such
specification, the packet filtering problem is known to be constant time
(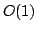 ). We propose to represent the first-order logic formula as Interval Decision Diagrams. This structure has several advantages. First,
the algorithm for removing redundancy and unnecessary tests is very simple.
Secondly, it allows us to handle integer variables which makes it efficient
on a generic CPUs. And, finally, we introduce an extension of IDDs called
Multi-Terminal Interval Decision Diagrams in order to deal with any
number of policies. ). We propose to represent the first-order logic formula as Interval Decision Diagrams. This structure has several advantages. First,
the algorithm for removing redundancy and unnecessary tests is very simple.
Secondly, it allows us to handle integer variables which makes it efficient
on a generic CPUs. And, finally, we introduce an extension of IDDs called
Multi-Terminal Interval Decision Diagrams in order to deal with any
number of policies.
In matter of efficiency, we evaluate the
performance our framework through a prototype toolkit composed by a compiler and a packet filter. The results of the experiments shows
that this method is efficient in terms of CPU usage and has a low storage
requirements.
Finally, we outline a tool, called Network Access
Verifier. This tool demonstrates how the IDD representation can be used for
verifying access properties of a network. In total, potentially improving the
security of a network.
- RS-02-42
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Luca Aceto, Jens Alsted Hansen, Anna
Ingólfsdóttir, Jacob Johnsen, and John Knudsen.
Checking Consistency of Pedigree Information is NP-complete
(Preliminary Report).
October 2002.
16 pp. Superseeded by RS-03-17.
Abstract: Consistency checking is a fundamental computational
problem in genetics. Given a pedigree and information on the genotypes of
some of the individuals in it, the aim of consistency checking is to
determine whether these data are consistent with the classic Mendelian laws
of inheritance. This problem arose originally from the geneticists' need to
filter their input data from erroneous information, and is well motivated
from both a biological and a sociological viewpoint. This paper shows that
consistency checking is NP-complete, even in the presence of three alleles.
Several other results on the computational complexity of problems from
genetics that are related to consistency checking are also offered. In
particular, it is shown that checking the consistency of pedigrees over two
alleles can be done in polynomial time.
- RS-02-41
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Stephen L. Bloom and Zoltán Ésik.
Axiomatizing Omega and Omega-op Powers of Words.
October 2002.
16 pp.
Abstract: In 1978, Courcelle asked for a complete set of axioms
and rules for the equational theory of (discrete regular) words equipped with
the operations of product, omega power and omega-op power. In this paper we
find a simple set of equations and prove they are complete. Moreover, we show
that the equational theory is decidable in polynomial time.
- RS-02-40
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Luca Aceto, Willem Jan Fokkink, and Anna
Ingólfsdóttir.
A Note on an Expressiveness Hierarchy for Multi-exit Iteration.
September 2002.
8 pp. Appears in Information Processing Letters, Elsevier,
87(1):17-23, 2003.
Abstract: Multi-exit iteration is a generalization of the
standard binary Kleene star operation that allows for the specification of
agents that, up to bisimulation equivalence, are solutions of systems of
recursion equations of the form
where 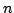 is a positive integer, and the is a positive integer, and the
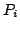 and the and the 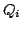 are process terms. The addition of multi-exit iteration
to Basic Process Algebra (BPA) yields a more expressive language than that
obtained by augmenting BPA with the standard binary Kleene star. This note
offers an expressiveness hierarchy, modulo bisimulation equivalence, for the
family of multi-exit iteration operators proposed by Bergstra, Bethke and
Ponse. are process terms. The addition of multi-exit iteration
to Basic Process Algebra (BPA) yields a more expressive language than that
obtained by augmenting BPA with the standard binary Kleene star. This note
offers an expressiveness hierarchy, modulo bisimulation equivalence, for the
family of multi-exit iteration operators proposed by Bergstra, Bethke and
Ponse.
- RS-02-39
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Stephen L. Bloom and Zoltán Ésik.
Some Remarks on Regular Words.
September 2002.
27 pp.
Abstract: In the late 1970's, Courcelle introduced the class of
``arrangements'', or labeled linear ordered sets, here called just ``words''.
He singled out those words which are solutions of finite systems of fixed
point equations involving finite words, which we call the ``regular words''.
The current paper contains some new descriptions of this class of words
related to properties of regular sets of binary strings, and uses finite
automata to decide various natural questions concerning these words. In
particular we show that a countable word is regular iff it can be defined on
an ordinary regular language (which can be chosen to be a prefix code)
ordered by the lexicographical order such that the labeling function
satisfies a regularity condition. Those regular words whose underlying order
is ``discrete'' or ``scattered'' are characterized in several ways.
- RS-02-38
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Daniele Varacca.
The Powerdomain of Indexed Valuations.
September 2002.
54 pp. Short version appears in Plotkin, editor, Seventeenth
Annual IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science, Lics '02
Proceedings, 2002, pages 299-308.
Abstract: This paper is about combining nondeterminism and
probabilities. We study this phenomenon from a domain theoretic point of
view. In domain theory, nondeterminism is modeled using the notion of
powerdomain, while probability is modeled using the powerdomain of
valuations. Those two functors do not combine well, as they are. We define
the notion of powerdomain of indexed valuations, which can be combined nicely
with the usual nondeterministic powerdomain. We show an equational
characterization of our construction. Finally we discuss the computational
meaning of indexed valuations, and we show how they can be used, by giving a
denotational semantics of a simple imperative language.
- RS-02-37
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Mads Sig Ager, Olivier Danvy, and Mayer
Goldberg.
A Symmetric Approach to Compilation and Decompilation.
August 2002.
45 pp. Appears in Mogensen, Schmidt and Sudborough, editors, The
Essence of Computation: Complexity, Analysis, Transformation, LNCS 2556,
2002, pages 296-331.
Abstract: Just as specializing a source interpreter can achieve
compilation from a source language to a target language, we observe that
specializing a target interpreter can achieve compilation from the target
language to the source language. In both cases, the key issue is the choice
of whether to perform an evaluation or to emit code that represents this
evaluation.
We substantiate this observation by specializing two
source interpreters and two target interpreters. We first consider a source
language of arithmetic expressions and a target language for a stack machine,
and then the lambda-calculus and the SECD-machine language. In each case, we
prove that the target-to-source compiler is a left inverse of the
source-to-target compiler, i.e., it is a decompiler.
In the context of
partial evaluation, compilation by source-interpreter specialization is
classically referred to as a Futamura projection. By symmetry, it seems
logical to refer to decompilation by target-interpreter specialization as a
Futamura embedding.
- RS-02-36
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Daniel Damian and Olivier Danvy.
CPS Transformation of Flow Information, Part II:
Administrative Reductions.
August 2002.
9 pp. To appear in the Journal of Functional Programming. This
report supersedes the earlier BRICS report RS-01-40.
Abstract: We characterize the impact of a linear 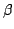 -reduction on the result of a control-flow analysis. (By ``a linear -reduction on the result of a control-flow analysis. (By ``a linear
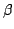 -reduction'' we mean the -reduction'' we mean the 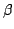 -reduction of a linear -reduction of a linear 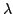 -abstraction, i.e., of a -abstraction, i.e., of a 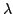 -abstraction whose parameter occurs
exactly once in its body.) -abstraction whose parameter occurs
exactly once in its body.)
As a corollary, we consider the
administrative reductions of a Plotkin-style transformation into
continuation-passing style (CPS), and how they affect the result of a
constraint-based control-flow analysis and, in particular, the least element
in the space of solutions. We show that administrative reductions preserve
the least solution. Preservation of least solutions solves a problem that was
left open in Palsberg and Wand's article ``CPS Transformation of Flow
Information.''
Together, Palsberg and Wand's article and the present
article show how to map in linear time the least solution of the flow
constraints of a program into the least solution of the flow constraints of
the CPS counterpart of this program, after administrative reductions.
Furthermore, we show how to CPS transform control-flow information in one
pass.
- RS-02-35
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Patricia Bouyer.
Timed Automata May Cause Some Troubles.
August 2002.
44 pp.
Abstract: Timed automata are a widely studied model. Its
decidability has been proved using the so-called region automaton
construction. This construction provides a correct abstraction for the
behaviours of timed automata, but it does not support a natural
implementation and, in practice, algorithms based on the notion of zones are
implemented using adapted data structures like DBMs. When we focus on forward
analysis algorithms, the exact computation of all the successors of the
initial configurations does not always terminate. Thus, some abstractions are
often used to ensure termination, among which, a widening operator on
zones.
In this paper, we study in details this widening operator and
the forward analysis algorithm that uses it. This algorithm is most used and
implemented in tools like Kronos and Uppaal. One of our main results is that
it is hopeless to find a forward analysis algorithm, that uses such a
widening operator, and which is correct. This goes really against what one
could think. We then study in details this algorithm in the more general
framework of updatable timed automata, a model which has been introduced as a
natural syntactic extension of classical timed automata. We describe
subclasses of this model for which a correct widening operator can be found.
- RS-02-34
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Morten Rhiger.
A Foundation for Embedded Languages.
August 2002.
29 pp. To appear in TOPLAS, ACM Transactions on Programming
Languages and Systems.
Abstract: Recent work on embedding object languages into
Haskell use ``phantom types'' (i.e., parameterized types whose parameter does
not occur on the right-hand side of the type definition) to ensure that the
embedded object-language terms are simply typed. But is it a safe assumption
that only simply-typed terms can be represented in Haskell using
phantom types? And conversely, can all simply-typed terms be
represented in Haskell under the restrictions imposed by phantom types? In
this article we investigate the conditions under which these assumptions are
true: We show that these questions can be answered affirmatively for an
idealized Haskell-like language and discuss to which extent Haskell can be
used as a meta-language.
- RS-02-33
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Vincent Balat and Olivier Danvy.
Memoization in Type-Directed Partial Evaluation.
July 2002.
18 pp. Appears in Batory, Consel and Taha, editors, ACM
SIGPLAN/SIGSOFT Conference on Generative Programming and Component
Engineering, GPCE '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2487, 2002, pages 78-92.
Abstract: We use a code generator--type-directed partial
evaluation--to verify conversions between isomorphic types, or more
precisely to verify that a composite function is the identity function at
some complicated type. A typed functional language such as ML provides a
natural support to express the functions and type-directed partial evaluation
provides a convenient setting to obtain the normal form of their composition.
However, off-the-shelf type-directed partial evaluation turns out to yield
gigantic normal forms.
We identify that this gigantism is due to
redundancies, and that these redundancies originate in the handling of sums,
which uses delimited continuations. We successfully eliminate these
redundancies by extending type-directed partial evaluation with memoization
capabilities. The result only works for pure functional programs, but it
provides an unexpected use of code generation and it yields
orders-of-magnitude improvements both in time and in space for type
isomorphisms.
- RS-02-32
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Mads Sig Ager, Olivier Danvy, and
Henning Korsholm Rohde.
On Obtaining Knuth, Morris, and Pratt's String Matcher by
Partial Evaluation.
July 2002.
43 pp. Appears in Chin, editor, ACM SIGPLAN ASIAN Symposium on
Partial Evaluation and Semantics-Based Program Manipulation, ASIA-PEPM '02
Proceedings, 2002, pages 32-46.
Abstract: We present the first formal proof that partial
evaluation of a quadratic string matcher can yield the precise behaviour of
Knuth, Morris, and Pratt's linear string matcher.
Obtaining a KMP-like
string matcher is a canonical example of partial evaluation: starting from
the naive, quadratic program checking whether a pattern occurs in a text, one
ensures that backtracking can be performed at partial-evaluation time (a
binding-time shift that yields a staged string matcher); specializing the
resulting staged program yields residual programs that do not back up on the
text, a la KMP. We are not aware, however, of any formal proof that partial
evaluation of a staged string matcher precisely yields the KMP string
matcher, or in fact any other specific string matcher.
In this
article, we present a staged string matcher and we formally prove that it
performs the same sequence of comparisons between pattern and text as the KMP
string matcher. To this end, we operationally specify each of the programming
languages in which the matchers are written, and we formalize each sequence
of comparisons with a trace semantics. We also state the (mild) conditions
under which specializing the staged string matcher with respect to a pattern
string provably yields a specialized string matcher whose size is
proportional to the length of this pattern string and whose time complexity
is proportional to the length of the text string. Finally, we show how
tabulating one of the functions in this staged string matcher gives rise to
the `next' table of the original KMP algorithm.
The method scales for
obtaining other linear string matchers, be they known or new.
- RS-02-31
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Kohlenbach and Paulo B. Oliva.
Proof Mining: A Systematic Way of Analysing Proofs in
Mathematics.
June 2002.
47 pp. Appears in Proceedings of the Steklov Institute of
Mathematics, 242:136-164, 2003.
Abstract: We call proof mining the process of logically
analyzing proofs in mathematics with the aim of obtaining new information. In
this survey paper we discuss, by means of examples from mathematics, some of
the main techniques used in proof mining. We show that those techniques not
only apply to proofs based on classical logic, but also to proofs which
involve non-effective principles such as the attainment of the infimum of
![$f\in C[0,1]$](img18.gif) and the convergence for bounded monotone sequences of reals. We
also report on recent case studies in approximation theory and fixed point
theory where new results were obtained. and the convergence for bounded monotone sequences of reals. We
also report on recent case studies in approximation theory and fixed point
theory where new results were obtained.
- RS-02-30
-
Olivier Danvy and Ulrik P. Schultz.
Lambda-Lifting in Quadratic Time.
June 2002.
17 pp. Appears in Hu and Rodríguez-Artalejo, editors, Sixth
International Symposium on Functional and Logic Programming, FLOPS '02
Proceedings, LNCS 2441, 2002, pages 134-151. Superseeded by the BRICS report
RS-03-26.
Abstract: Lambda-lifting is a program transformation used in
compilers and in partial evaluators and that operates in cubic time. In this
article, we show how to reduce this complexity to quadratic time.
Lambda-lifting transforms a block-structured program into a set of recursive
equations, one for each local function in the source program. Each equation
carries extra parameters to account for the free variables of the
corresponding local function and of all its callees. It is the search for
these extra parameters that yields the cubic factor in the traditional
formulation of lambda-lifting, which is due to Johnsson. This search is
carried out by a transitive closure.
Instead, we partition the call
graph of the source program into strongly connected components, based on the
simple observation that all functions in each component need the same extra
parameters and thus a transitive closure is not needed. We therefore simplify
the search for extra parameters by treating each strongly connected component
instead of each function as a unit, thereby reducing the time complexity of
lambda-lifting from O(n3logn) to O(n2logn), where n is the size of the
program.
- RS-02-29
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Christian N. S. Pedersen and Tejs
Scharling.
Comparative Methods for Gene Structure Prediction in Homologous
Sequences.
June 2002.
20 pp. Appears in Guigó and Gusfield, editors, Algorithms in
Bioinformatics: 2nd International Workshop, WABI '02 Proceedings,
LNCS 2452, 2002, pages 220-234.
Abstract: The increasing number of sequenced genomes motivates
the use of evolutionary patterns to detect genes. We present a series of
comparative methods for gene finding in homologous prokaryotic or eukaryotic
sequences. Based on a model of legal genes and a similarity measure between
genes, we find the pair of legal genes of maximum similarity. We develop
methods based on genes models and alignment based similarity measures of
increasing complexity, which take into account many details of real gene
structures, e.g. the similarity of the proteins encoded by the exons. When
using a similarity measure based on an exiting alignment, the methods run in
linear time. When integrating the alignment and prediction process which
allows for more fine grained similarity measures, the methods run in
quadratic time. We evaluate the methods in a series of experiments on
synthetic and real sequence data, which show that all methods are competitive
but that taking the similarity of the encoded proteins into account really
boost the performance.
- RS-02-28
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Kohlenbach and Laurentiu
Leustean.
Mann Iterates of Directionally Nonexpansive Mappings in
Hyperbolic Spaces.
June 2002.
33 pp. To appear in Abstract and Applied Analysis.
Abstract: In a previous paper, the first author derived an
explicit quantitative version of a theorem due to Borwein, Reich and Shafrir
on the asymptotic behaviour of Mann iterations of nonexpansive mappings of
convex sets 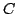 in normed linear spaces. This quantitative version, which was
obtained by a logical analysis of the ineffective proof given by Borwein,
Reich and Shafrir, could be used to obtain strong uniform bounds on the
asymptotic regularity of such iterations in the case of bounded in normed linear spaces. This quantitative version, which was
obtained by a logical analysis of the ineffective proof given by Borwein,
Reich and Shafrir, could be used to obtain strong uniform bounds on the
asymptotic regularity of such iterations in the case of bounded 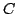 and even
weaker conditions. In this paper we extend these results to hyperbolic spaces
and directionally nonexpansive mappings. In particular, we obtain
significantly stronger and more general forms of the main results of a recent
paper by W.A. Kirk with explicit bounds. As a special feature of our
approach, which is based on logical analysis instead of functional analysis,
no functional analytic embeddings are needed to obtain our uniformity results
which contain all previously known results of this kind as special cases. and even
weaker conditions. In this paper we extend these results to hyperbolic spaces
and directionally nonexpansive mappings. In particular, we obtain
significantly stronger and more general forms of the main results of a recent
paper by W.A. Kirk with explicit bounds. As a special feature of our
approach, which is based on logical analysis instead of functional analysis,
no functional analytic embeddings are needed to obtain our uniformity results
which contain all previously known results of this kind as special cases.
- RS-02-27
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Anna Östlin and Rasmus Pagh.
Simulating Uniform Hashing in Constant Time and Optimal Space.
2002.
11 pp.
Abstract: Many algorithms and data structures employing hashing
have been analyzed under the uniform hashing assumption, i.e., the
assumption that hash functions behave like truly random functions. In this
paper it is shown how to implement hash functions that can be evaluated on a
RAM in constant time, and behave like truly random functions on any set of
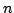 inputs, with high probability. The space needed to represent a function
is inputs, with high probability. The space needed to represent a function
is 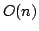 words, which is the best possible (and a polynomial improvement
compared to previous fast hash functions). As a consequence, a broad class of
hashing schemes can be implemented to meet, with high probability, the
performance guarantees of their uniform hashing analysis. words, which is the best possible (and a polynomial improvement
compared to previous fast hash functions). As a consequence, a broad class of
hashing schemes can be implemented to meet, with high probability, the
performance guarantees of their uniform hashing analysis.
- RS-02-26
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Margarita Korovina.
Fixed Points on Abstract Structures without the Equality Test.
June 2002.
14 pp. Appears in Vardi and Voronko, editors, Logic for
Programming, Artificial Intelligence, and Reasoning, 10th International
Conference, LPAR '03 Proceedings, LNCS 2860, 2003, pages 290-301.
Appeared earlier in Ésik and Ingólfsdóttir, editors, Preliminary Proceedings of the Workshop on Fixed Points in Computer Science,
FICS '02, (Copenhagen, Denmark, July 20 and 21, 2002), BRICS Notes
Series NS-02-2, 2002, pages 58-61.
Abstract: In this paper we present a study of definability
properties of fixed points of effective operators on abstract structures
without the equality test. In particular we prove that Gandy theorem holds
for abstract structures. This provides a useful tool for dealing with
recursive definitions using 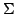 -formulas. -formulas.
One of the applications
of Gandy theorem in the case of the reals without the equality test is that
it allows us to define universal 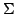 -predicates. It leads to a
topological characterisation of -predicates. It leads to a
topological characterisation of 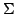 -relations on -relations on 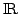 . .
- RS-02-25
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Hans Hüttel.
Deciding Framed Bisimilarity.
May 2002.
20 pp. Appears in Antonín and Mayr, editors, 4th
International Workshop on Verification of Infinite-State Systems,
INFINITY '02 Proceedings, ENTCS 68(6), 2002, 18 pp.
Abstract: The spi-calculus, proposed by Abadi and Gordon, is a
process calculus based on the 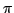 -calculus and is intended for reasoning
about the behaviour of cryptographic protocols. We consider the
finite-control fragment of the spi-calculus, showing it to be Turing-powerful
(a result which is joint work with Josva Kleist, Uwe Nestmann, and Björn
Victor.) Next, we restrict our attention to finite (non-recursive)
spi-calculus. Here, we show that framed bisimilarity, an equivalence relation
proposed by Abadi and Gordon, showing that it is decidable for this fragment. -calculus and is intended for reasoning
about the behaviour of cryptographic protocols. We consider the
finite-control fragment of the spi-calculus, showing it to be Turing-powerful
(a result which is joint work with Josva Kleist, Uwe Nestmann, and Björn
Victor.) Next, we restrict our attention to finite (non-recursive)
spi-calculus. Here, we show that framed bisimilarity, an equivalence relation
proposed by Abadi and Gordon, showing that it is decidable for this fragment.
- RS-02-24
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Aske Simon Christensen, Anders Møller,
and Michael I. Schwartzbach.
Static Analysis for Dynamic XML.
May 2002.
13 pp.
Abstract: We describe the summary graph lattice for
dataflow analysis of programs that dynamically construct XML documents.
Summary graphs have successfully been used to provide static guarantees in
the JWIG language for programming interactive Web services. In particular,
the JWIG compiler is able to check validity of dynamically generated XHTML
documents and to type check dynamic form data. In this paper we present
summary graphs and indicate their applicability for various scenarios. We
also show that summary graphs have exactly the same expressive power as the
regular expression types from XDuce, but that the extra structure in summary
graphs makes them more suitable for certain program analyses.
- RS-02-23
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Antonio Di Nola and Laurentiu
Leustean.
Compact Representations of BL-Algebras.
May 2002.
25 pp.
Abstract: In this paper we define sheaf spaces of BL-algebras
(or BL-sheaf spaces), we study completely regular and compact BL-sheaf spaces
and compact representations of BL-algebras and, finally, we prove that the
category of non-trivial BL-algebras is equivalent with the category of
compact local BL-sheaf spaces.
- RS-02-22
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Mogens Nielsen, Catuscia Palamidessi, and
Frank D. Valencia.
On the Expressive Power of Concurrent Constraint Programming
Languages.
May 2002.
34 pp. Appears in Pfenning, editor, 4th International Conference
on Principles and Practice of Declarative Programming, PPDP '02
Proceedings, 2002, pages 156-157.
Abstract: The tcc paradigm is a formalism for timed concurrent
constraint programming. Several tcc languages differing in their way of
expressing infinite behaviour have been proposed in the literature. In this
paper we study the expressive power of some of these languages. In
particular, we show that:
- (1)
- recursive procedures
with parameters can be encoded into parameterless recursive procedures with
dynamic scoping, and vice-versa.
- (2)
- replication can be encoded into
parameterless recursive procedures with static scoping, and vice-versa.
- (3)
- the languages from (1) are strictly more expressive than the
languages from (2).
Furthermore, we show that behavioural
equivalence is undecidable for the languages from (1), but decidable for the
languages from (2). The undecidability result holds even if the process
variables take values from a fixed finite domain.
- RS-02-21
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Zoltán Ésik and Werner Kuich.
Formal Tree Series.
April 2002.
66 pp.
Abstract: In this survey we generalize some results on formal
tree languages, tree grammars and tree automata by an algebraic treatment
using semirings, fixed point theory, formal tree series and matrices. The use
of these mathematical constructs makes definitions, constructions, and proofs
more satisfactory from an mathematical point of view than the customary ones.
The contents of this survey paper is indicated by the titles of the sections:
- 1.
- Introduction
- 2.
- Preliminaries
- 3.
- Tree
automata and systems of equations
- 4.
- Closure properties and a Kleene
Theorem for recognizable tree series
- 5.
- Pushdown tree automata,
algebraic tree systems, and a Kleene Theorem
- 6.
- Tree series
transducers
- 7.
- Full abstract families of tree series
- 8.
- Connections to formal power series
.
- RS-02-20
-
Zoltán Ésik and Kim G. Larsen.
Regular Languages Definable by Lindström Quantifiers
(Preliminary Version).
April 2002.
56 pp. Superseeded by the BRICS report
RS-03-28.
Abstract: In our main result, we establish a formal connection
between Lindström quantifiers with respect to regular languages and the
double semidirect product of finite monoid-generator pairs. We use this
correspondence to characterize the expressive power of Lindström
quantifiers associated with a class of regular languages.
- RS-02-19
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Stephen L. Bloom and Zoltán Ésik.
An Extension Theorem with an Application to Formal Tree Series.
April 2002.
51 pp. Appears in Blute and Selinger, editors, Category Theory
and Computer Science: 9th International Conference, CTCS '02 Proceedings,
ENTCS 69, 2003 under the title Unique Guarded Fixed Points in an
Additive Setting.
Abstract: A grove theory is a Lawvere algebraic theory 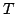 for
which each hom-set for
which each hom-set 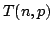 is a commutative monoid; composition on the right
distrbutes over all finite sums: is a commutative monoid; composition on the right
distrbutes over all finite sums:
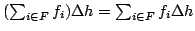 . A matrix theory is a grove theory in which composition on
the left and right distributes over finite sums. A matrix theory . A matrix theory is a grove theory in which composition on
the left and right distributes over finite sums. A matrix theory 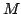 is
isomorphic to a theory of all matrices over the semiring is
isomorphic to a theory of all matrices over the semiring 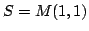 . Examples
of grove theories are theories of (bisimulation equivalence classes of)
synchronization trees, and theories of formal tree series over a semiring . Examples
of grove theories are theories of (bisimulation equivalence classes of)
synchronization trees, and theories of formal tree series over a semiring
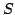 . Our main theorem states that if . Our main theorem states that if 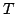 is a grove theory which has a matrix
subtheory is a grove theory which has a matrix
subtheory 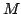 which is an iteration theory, then, under certain conditions,
the fixed point operation on which is an iteration theory, then, under certain conditions,
the fixed point operation on 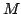 can be extended in exactly one way to a
fixedpoint operation on can be extended in exactly one way to a
fixedpoint operation on 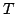 such that such that 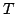 is an iteration theory. A second
theorem is a Kleene-type result. Assume that is an iteration theory. A second
theorem is a Kleene-type result. Assume that 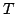 is a iteration grove theory
and is a iteration grove theory
and 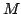 is a sub iteration grove theory of is a sub iteration grove theory of 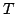 which is a matrix theory. For
a given collection which is a matrix theory. For
a given collection 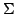 of scalar morphisms in of scalar morphisms in 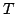 we describe the
smallest sub iteration grove theory of we describe the
smallest sub iteration grove theory of 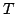 containing all the morphisms in containing all the morphisms in
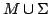 . .
- RS-02-18
-
Gerth Stølting Brodal and Rolf Fagerberg.
Cache Oblivious Distribution Sweeping.
April 2002.
Appears in Widmayer, Triguero, Morales, Hennessy, Eidenbenz and
Conejo, editors, 29th International Colloquium on Automata, Languages,
and Programming, ICALP '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2380, 2002, pages 426-438.
Abstract: We adapt the distribution sweeping method to the
cache oblivious model. Distribution sweeping is the name used for a general
approach for divide-and-conquer algorithms where the combination of solved
subproblems can be viewed as a merging process of streams. We demonstrate by
a series of algorithms for specific problems the feasibility of the method in
a cache oblivious setting. The problems all come from computational geometry,
and are: orthogonal line segment intersection reporting, the all nearest
neighbors problem, the 3D maxima problem, computing the measure of a set of
axis-parallel rectangles, computing the visibility of a set of line segments
from a point, batched orthogonal range queries, and reporting pairwise
intersections of axis-parallel rectangles. Our basic building block is a
simplified version of the cache oblivious sorting algorithm Funnelsort of
Frigo et al., which is of independent interest.
- RS-02-17
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Bolette Ammitzbøll Madsen,
Jesper Makholm Byskov, and Bjarke Skjernaa.
On the Number of Maximal Bipartite Subgraphs of a Graph.
April 2002.
7 pp.
Abstract: We show new lower and upper bounds on the number of
maximal induced bipartite subgraphs of graphs with 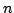 vertices. We present
an infinite family of graphs having vertices. We present
an infinite family of graphs having
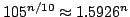 such
subgraphs, which improves an earlier lower bound by Schiermeyer (1996). We
show an upper bound of such
subgraphs, which improves an earlier lower bound by Schiermeyer (1996). We
show an upper bound of
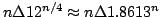 and give an
algorithm that lists all maximal induced bipartite subgraphs in time
proportional to this bound. This is used in an algorithm for checking
4-colourability of a graph running within the same time bound. and give an
algorithm that lists all maximal induced bipartite subgraphs in time
proportional to this bound. This is used in an algorithm for checking
4-colourability of a graph running within the same time bound.
- RS-02-16
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Jirí Srba.
Strong Bisimilarity of Simple Process Algebras: Complexity Lower
Bounds.
April 2002.
33 pp. To appear in Acta Informatica.
Abstract: In this paper we study bisimilarity problems for
simple process algebras. In particular, we show PSPACE-hardness of the
following problems:
- strong bisimilarity of Basic
Parallel Processes (BPP),
- strong bisimilarity of Basic Process Algebra
(BPA),
- strong regularity of BPP, and
- strong regularity of BPA.
We also demonstrate NL-hardness of strong regularity problems
for the normed subclasses of BPP and BPA.
Bisimilarity problems for
simple process algebras are introduced in a general framework of process
rewrite systems, and a uniform description of the new techniques used for the
hardness proofs is provided.
- RS-02-15
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Jesper Makholm Nielsen.
On the Number of Maximal Independent Sets in a Graph.
April 2002.
10 pp.
Abstract: We show that the number of maximal independent sets
of size exactly 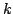 in any graph of size in any graph of size 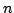 is at most is at most
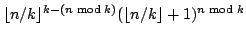 . For maximal
independent sets of size at most . For maximal
independent sets of size at most 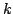 the same bound holds for the same bound holds for 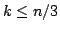 . For . For 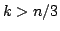 a bound of approximately a bound of approximately 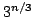 is given. All the bounds
are exactly tight and improve Eppstein (2001) who give the bound is given. All the bounds
are exactly tight and improve Eppstein (2001) who give the bound
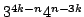 on the number of maximal independent sets of size at most on the number of maximal independent sets of size at most
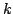 , which is the same for , which is the same for
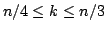 , but larger otherwise. We
give an algorithm listing the maximal independent sets in a graph in time
proportional to these bounds (ignoring a polynomial factor), and we use this
algorithm to construct algorithms for 4- and 5- colouring running in time , but larger otherwise. We
give an algorithm listing the maximal independent sets in a graph in time
proportional to these bounds (ignoring a polynomial factor), and we use this
algorithm to construct algorithms for 4- and 5- colouring running in time
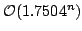 and and
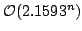 , respectively. , respectively.
- RS-02-14
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Berger and Paulo B. Oliva.
Modified Bar Recursion.
April 2002.
23 pp. To appear in Lecture Notes in Logic.
Abstract: We introduce a variant of Spector's bar recursion
(called ``modified bar recursion'') in finite types to give a realizability
interpretation of the classical axiom of countable choice allowing for the
extraction of witnesses from proofs of 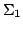 formulas in classical
analysis. As a second application of modified bar recursion we present a bar
recursive definition of the fan functional. Moreover, we show that modified
bar recursion exists in formulas in classical
analysis. As a second application of modified bar recursion we present a bar
recursive definition of the fan functional. Moreover, we show that modified
bar recursion exists in 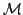 (the model of strongly majorizable
functionals) and is not S1-S9 computable in (the model of strongly majorizable
functionals) and is not S1-S9 computable in 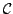 (the model of total
functionals). Finally, we show that modified bar recursion defines Spector's
bar recursion primitive recursively. (the model of total
functionals). Finally, we show that modified bar recursion defines Spector's
bar recursion primitive recursively.
- RS-02-13
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Gerth Stølting Brodal, Rune B.
Lyngsø, Anna Östlin, and Christian N. S. Pedersen.
Solving the String Statistics Problem in Time 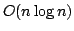 . .
March 2002.
28 pp. Shorter version appears in Widmayer, Triguero, Morales,
Hennessy, Eidenbenz and Conejo, editors, 29th International Colloquium
on Automata, Languages, and Programming, ICALP '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2380,
2002, pages 728-739.
Abstract: The string statistics problem consists of
preprocessing a string of length 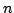 such that given a query pattern of
length such that given a query pattern of
length 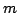 , the maximum number of non-overlapping occurrences of the query
pattern in the string can be reported efficiently. Apostolico and Preparata
introduced the minimal augmented suffix tree (MAST) as a data structure for
the string statistics problem, and showed how to construct the MAST in time , the maximum number of non-overlapping occurrences of the query
pattern in the string can be reported efficiently. Apostolico and Preparata
introduced the minimal augmented suffix tree (MAST) as a data structure for
the string statistics problem, and showed how to construct the MAST in time
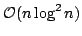 and how it supports queries in time and how it supports queries in time 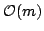 for
constant sized alphabets. A subsequent theorem by Fraenkel and Simpson
stating that a string has at most a linear number of distinct squares implies
that the MAST requires space for
constant sized alphabets. A subsequent theorem by Fraenkel and Simpson
stating that a string has at most a linear number of distinct squares implies
that the MAST requires space 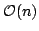 . In this paper we improve the
construction time for the MAST to . In this paper we improve the
construction time for the MAST to
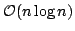 by extending the
algorithm of Apostolico and Preparata to exploit properties of efficient
joining and splitting of search trees together with a refined analysis. by extending the
algorithm of Apostolico and Preparata to exploit properties of efficient
joining and splitting of search trees together with a refined analysis.
- RS-02-12
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy and Mayer Goldberg.
There and Back Again.
March 2002.
ii+11 pp. Appears in Peyton Jones, editor, Proceedings of the
7th ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Functional Programming, 2002,
pages 230-234. This report supersedes the earlier report BRICS RS-01-39.
Abstract: We present a programming pattern where a recursive
function traverses a data structure--typically a list--at return time. The
idea is that the recursive calls get us there (typically to a base case) and
the returns get us back again while traversing the data structure. We
name this programming pattern of traversing a data structure at return time
``There And Back Again'' (TABA).
The TABA pattern directly applies to
computing a symbolic convolution. It also synergizes well with other
programming patterns, e.g., dynamic programming and traversing a list at
double speed. We illustrate TABA and dynamic programming with Catalan
numbers. We illustrate TABA and traversing a list at double speed with
palindromes and we obtain a novel solution to this traditional
exercise.
A TABA-based function written in direct style makes full use
of an Algol-like control stack and needs no heap allocation. Conversely, in a
TABA-based function written in continuation-passing style, the continuation
acts as a list iterator. In general, the TABA pattern saves one from
constructing intermediate lists in reverse order.
- RS-02-11
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Aske Simon Christensen, Anders Møller,
and Michael I. Schwartzbach.
Extending Java for High-Level Web Service Construction.
March 2002.
54 pp. To appear in ACM Transactions on Programming Languages
and Systems.
Abstract: We incorporate innovations from the <bigwig>
project into the Java language to provide high-level features for Web service
programming. The resulting language, JWIG, contains an advanced session model
and a flexible mechanism for dynamic construction of XML documents, in
particular XHTML. To support program development we provide a suite of
program analyses that at compile-time verify for a given program that no
run-time errors can occur while building documents or receiving form input,
and that all documents being shown are valid according to the document type
definition for XHTML 1.0.
We compare JWIG with Servlets and JSP which
are widely used Web service development platforms. Our implementation and
evaluation of JWIG indicate that the language extensions can simplify the
program structure and that the analyses are sufficiently fast and precise to
be practically useful.
- RS-02-10
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ulrich Kohlenbach.
Uniform Asymptotic Regularity for Mann Iterates.
March 2002.
17 pp. Appears in Journal of Mathematical Analysis and
Applications, 279(2):531-544, 2003.
Abstract: In a previous paper we obtained an effective
quantitative analysis of a theorem due to Borwein, Reich and Shafrir on the
asymptotic behavior of general Krasnoselski-Mann iterations for nonexpansive
self-mappings of convex sets 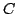 in arbitrary normed spaces. We used this
result to obtain a new strong uniform version of Ishikawa's theorem for
bounded in arbitrary normed spaces. We used this
result to obtain a new strong uniform version of Ishikawa's theorem for
bounded 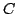 . In this paper we give a qualitative improvement of our result in
the unbounded case and prove the uniformity result for the bounded case under
the weaker assumption that . In this paper we give a qualitative improvement of our result in
the unbounded case and prove the uniformity result for the bounded case under
the weaker assumption that 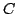 contains a point contains a point 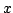 whose Krasnoselski-Mann
iteration whose Krasnoselski-Mann
iteration 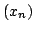 is bounded. is bounded.
We also consider more general iterations for
which asymptotic regularity is known only for uniformly convex spaces
(Groetsch). We give uniform effective bounds for (an extension of) Groetsch's
theorem which generalize previous results by Kirk/Martinez-Yanez and the
author.
- RS-02-9
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Anna Östlin and Rasmus Pagh.
One-Probe Search.
February 2002.
17 pp. Appears in Widmayer, Triguero, Morales, Hennessy, Eidenbenz
and Conejo, editors, 29th International Colloquium on Automata,
Languages, and Programming, ICALP '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2380, 2002, pages
439-450.
Abstract: We consider dictionaries that perform lookups by
probing a single word of memory, knowing only the size of the data
structure. We describe a randomized dictionary where a lookup returns the
correct answer with probability 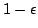 , and otherwise returns ``don't
know''. The lookup procedure uses an expander graph to select the memory
location to probe. Recent explicit expander constructions are shown to yield
space usage much smaller than what would be required using a deterministic
lookup procedure. Our data structure supports efficient deterministic
updates, exhibiting new probabilistic guarantees on dictionary running time. , and otherwise returns ``don't
know''. The lookup procedure uses an expander graph to select the memory
location to probe. Recent explicit expander constructions are shown to yield
space usage much smaller than what would be required using a deterministic
lookup procedure. Our data structure supports efficient deterministic
updates, exhibiting new probabilistic guarantees on dictionary running time.
- RS-02-8
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Ronald Cramer and Serge Fehr.
Optimal Black-Box Secret Sharing over Arbitrary Abelian Groups.
February 2002.
19 pp. Appears in Yung, editor, Advances in Cryptology: 22nd
Annual International Cryptology Conference, CRYPTO '02 Proceedings,
LNCS 2442, 2002, pages 272-287.
- RS-02-7
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Anna Ingólfsdóttir, Anders Lyhne
Christensen, Jens Alsted Hansen, Jacob Johnsen, John Knudsen, and Jacob Illum
Rasmussen.
A Formalization of Linkage Analysis.
February 2002.
vi+109 pp.
Abstract: In this report a formalization of genetic linkage
analysis is introduced. Linkage analysis is a computationally hard
biomathematical method, which purpose is to locate genes on the human genome.
It is rooted in the new area of bioinformatics and no formalization of the
method has previously been established. Initially, the biological model is
presented. On the basis of this biological model we establish a formalization
that enables reasoning about algorithms used in linkage analysis. The
formalization applies both for single and multi point linkage analysis. We
illustrate the usage of the formalization in correctness proofs of central
algorithms and optimisations for linkage analysis. A further use of the
formalization is to reason about alternative methods for linkage analysis. We
discuss the use of MTBDDs and PDGs in linkage analysis, since they have
proven efficient for other computationally hard problems involving large
state spaces. We conclude that none of the techniques discussed are directly
applicable to linkage analysis, however further research is needed in order
to investigated whether a modified version of one or more of these are
applicable.
- RS-02-6
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Luca Aceto, Zoltán Ésik, and Anna
Ingólfsdóttir.
Equational Axioms for Probabilistic Bisimilarity (Preliminary
Report).
February 2002.
22 pp. Appears in Kirchner and Ringeissen, editors, Algebraic
Methodology and Software Technology: 9th International Conference,
AMAST '02 Proceedings, LNCS 2422, 2002, pages 239-253.
Abstract: This paper gives an equational axiomatization of
probabilistic bisimulation equivalence for a class of finite-state agents
previously studied by Stark and Smolka ((2000) Proof, Language, and
Interaction: Essays in Honour of Robin Milner, pp. 571-595). The
axiomatization is obtained by extending the general axioms of iteration
theories (or iteration algebras), which characterize the equational
properties of the fixed point operator on (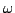 -)continuous or
monotonic functions, with three axiom schemas that express laws that are
specific to probabilistic bisimilarity. Hence probabilistic bisimilarity
(over finite-state agents) has an equational axiomatization relative to
iteration algebras. -)continuous or
monotonic functions, with three axiom schemas that express laws that are
specific to probabilistic bisimilarity. Hence probabilistic bisimilarity
(over finite-state agents) has an equational axiomatization relative to
iteration algebras.
- RS-02-5
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Federico Crazzolara and Glynn Winskel.
Composing Strand Spaces.
February 2002.
30 pp.
Abstract: The strand space model for the analysis of security
protocols is known to have some limitations in the patterns of nondeterminism
it allows and in the ways in which strand spaces can be composed. Its
successful application to a broad range of security protocols may therefore
seem surprising. This paper gives a formal explanation of the wide
applicability of strand spaces. We start with an extension of strand spaces
which permits several operations to be defined in a compositional way,
forming a process language for building up strand spaces. We then show, under
reasonable conditions how to reduce the extended strand spaces to ones of a
traditional kind. For security protocols we are mainly interested in their
safety properties. This suggests a strand-space equivalence: two strand
spaces are equivalent if and only if they have essentially the same sets of
bundles. However this equivalence is not a congruence with respect to the
strand-space operations. By extending the notion of bundle we show how to
define the strand-space operations directly on ``bundle spaces''. This leads
to a characterisation of the largest congruence within the strand-space
equivalence. Finally, we relate strand spaces to event structures, a well
known model for concurrency.
- RS-02-4
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy and Lasse R. Nielsen.
Syntactic Theories in Practice.
January 2002.
34 pp. This revised report supersedes the earlier BRICS report
RS-01-31.
Abstract: The evaluation function of a syntactic theory is
canonically defined as the transitive closure of (1) decomposing a program
into an evaluation context and a redex, (2) contracting this redex, and (3)
plugging the contractum in the context. Directly implementing this evaluation
function therefore yields an interpreter with a worst-case overhead, for each
step, that is linear in the size of the input program. We present sufficient
conditions over a syntactic theory to circumvent this overhead, by replacing
the composition of (3) plugging and (1) decomposing by a single
``refocusing'' function mapping a contractum and a context into a new context
and a new redex, if there are any. We also show how to construct such a
refocusing function, we prove its correctness, and we analyze its
complexity.
We illustrate refocusing with two examples: a
programming-language interpreter and a transformation into
continuation-passing style. As a byproduct, the time complexity of this
program transformation is mechanically changed from quadratic in the worst
case to linear.
- RS-02-3
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Olivier Danvy and Lasse R. Nielsen.
On One-Pass CPS Transformations.
January 2002.
18 pp.
Abstract: We bridge two distinct approaches to one-pass CPS
transformations, i.e., CPS transformations that reduce administrative redexes
at transformation time instead of in a post-processing phase. One approach is
compositional and higher-order, and is due to Appel, Danvy and Filinski, and
Wand, building on Plotkin's seminal work. The other is non-compositional and
based on a syntactic theory of the 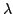 -calculus, and is due to Sabry
and Felleisen. To relate the two approaches, we use Church encoding,
Reynolds's defunctionalization, and an implementation technique for syntactic
theories, refocusing, developed in the second author's PhD thesis. -calculus, and is due to Sabry
and Felleisen. To relate the two approaches, we use Church encoding,
Reynolds's defunctionalization, and an implementation technique for syntactic
theories, refocusing, developed in the second author's PhD thesis.
This work is directly applicable to transforming programs into monadic normal
form.
- RS-02-2
-
PostScript,
PDF,
DVI.
Lasse R. Nielsen.
A Simple Correctness Proof of the Direct-Style Transformation.
January 2002.
11 pp.
Abstract: We build on Danvy and Nielsen's first-order program
transformation into continuation-passing style (CPS) to present a new
correctness proof of the converse transformation, i.e., a one-pass
transformation from CPS back to direct style. Previously published proofs
were based on, e.g., a one-pass higher-order CPS transformation, and were
complicated by having to reason about higher-order functions. In contrast,
this work is based on a one-pass CPS transformation that is both
compositional and first-order, and therefore the proof simply proceeds by
structural induction on syntax.
- RS-02-1
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Claus Brabrand, Anders Møller, and
Michael I. Schwartzbach.
The <bigwig> Project.
January 2002.
36 pp. This revised report supersedes the earlier BRICS report
RS-00-42.
Abstract: We present the results of the <bigwig> project,
which aims to design and implement a high-level domain-specific language for
programming interactive Web services.
A fundamental aspect of the
development of the World Wide Web during the last decade is the gradual
change from static to dynamic generation of Web pages. Generating Web pages
dynamically in dialogue with the client has the advantage of providing
up-to-date and tailor-made information. The development of systems for
constructing such dynamic Web services has emerged as a whole new research
area.
The <bigwig> language is designed by analyzing its
application domain and identifying fundamental aspects of Web services
inspired by problems and solutions in existing Web service development
languages. The core of the design consists of a session-centered service
model together with a flexible template-based mechanism for dynamic Web page
construction. Using specialized program analyses, certain Web specific
properties are verified at compile-time, for instance that only valid HTML
4.01 is ever shown to the clients. In addition, the design provides
high-level solutions to form field validation, caching of dynamic pages, and
temporal-logic based concurrency control, and it proposes syntax macros for
making highly domain-specific languages. The language is implemented via
widely available Web technologies, such as Apache on the server-side and
JavaScript and Java Applets on the client-side. We conclude with experience
and evaluation of the project.
|
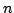 species based on pairwise distances between the species is a fundamental
problem in bioinformatics. Neighbor joining is a popular distance based tree
reconstruction method. It always proposes fully resolved binary trees despite
missing evidence in the underlying distance data. Distance based methods
based on the theory of Buneman trees and refined Buneman trees avoid this
problem by only proposing evolutionary trees whose edges satisfy a number of
constraints. These trees might not be fully resolved but there is strong
combinatorial evidence for each proposed edge. The currently best algorithm
for computing the refined Buneman tree from a given distance measure has a
running time of
species based on pairwise distances between the species is a fundamental
problem in bioinformatics. Neighbor joining is a popular distance based tree
reconstruction method. It always proposes fully resolved binary trees despite
missing evidence in the underlying distance data. Distance based methods
based on the theory of Buneman trees and refined Buneman trees avoid this
problem by only proposing evolutionary trees whose edges satisfy a number of
constraints. These trees might not be fully resolved but there is strong
combinatorial evidence for each proposed edge. The currently best algorithm
for computing the refined Buneman tree from a given distance measure has a
running time of 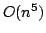 and a space consumption of
and a space consumption of 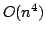 . In this paper,
we present an algorithm with running time
. In this paper,
we present an algorithm with running time 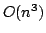 and space
consumption
and space
consumption 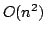 .
.
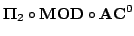 circuit can also be computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical nondeterministic branching program (or
cylindrical circuit) and that every function computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical circuit belongs to
circuit can also be computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical nondeterministic branching program (or
cylindrical circuit) and that every function computed by a constant width
polynomial size cylindrical circuit belongs to
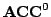 .
.
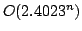 Using Maximal Independent
Sets.
Using Maximal Independent
Sets.
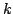 from our recent paper (2003), we prove that the running time is
from our recent paper (2003), we prove that the running time is
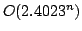 . Eppstein's algorithm runs in time
. Eppstein's algorithm runs in time 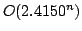 . The space
usage for both algorithms is
. The space
usage for both algorithms is 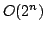 .
.
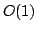 ). We propose to represent the first-order logic formula as Interval Decision Diagrams. This structure has several advantages. First,
the algorithm for removing redundancy and unnecessary tests is very simple.
Secondly, it allows us to handle integer variables which makes it efficient
on a generic CPUs. And, finally, we introduce an extension of IDDs called
Multi-Terminal Interval Decision Diagrams in order to deal with any
number of policies.
). We propose to represent the first-order logic formula as Interval Decision Diagrams. This structure has several advantages. First,
the algorithm for removing redundancy and unnecessary tests is very simple.
Secondly, it allows us to handle integer variables which makes it efficient
on a generic CPUs. And, finally, we introduce an extension of IDDs called
Multi-Terminal Interval Decision Diagrams in order to deal with any
number of policies.
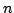 is a positive integer, and the
is a positive integer, and the
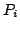 and the
and the 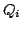 are process terms. The addition of multi-exit iteration
to Basic Process Algebra (BPA) yields a more expressive language than that
obtained by augmenting BPA with the standard binary Kleene star. This note
offers an expressiveness hierarchy, modulo bisimulation equivalence, for the
family of multi-exit iteration operators proposed by Bergstra, Bethke and
Ponse.
are process terms. The addition of multi-exit iteration
to Basic Process Algebra (BPA) yields a more expressive language than that
obtained by augmenting BPA with the standard binary Kleene star. This note
offers an expressiveness hierarchy, modulo bisimulation equivalence, for the
family of multi-exit iteration operators proposed by Bergstra, Bethke and
Ponse.
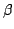 -reduction on the result of a control-flow analysis. (By ``a linear
-reduction on the result of a control-flow analysis. (By ``a linear
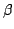 -reduction'' we mean the
-reduction'' we mean the 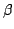 -reduction of a linear
-reduction of a linear 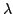 -abstraction, i.e., of a
-abstraction, i.e., of a 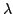 -abstraction whose parameter occurs
exactly once in its body.)
-abstraction whose parameter occurs
exactly once in its body.)![$f\in C[0,1]$](img18.gif) and the convergence for bounded monotone sequences of reals. We
also report on recent case studies in approximation theory and fixed point
theory where new results were obtained.
and the convergence for bounded monotone sequences of reals. We
also report on recent case studies in approximation theory and fixed point
theory where new results were obtained.
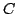 in normed linear spaces. This quantitative version, which was
obtained by a logical analysis of the ineffective proof given by Borwein,
Reich and Shafrir, could be used to obtain strong uniform bounds on the
asymptotic regularity of such iterations in the case of bounded
in normed linear spaces. This quantitative version, which was
obtained by a logical analysis of the ineffective proof given by Borwein,
Reich and Shafrir, could be used to obtain strong uniform bounds on the
asymptotic regularity of such iterations in the case of bounded 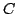 and even
weaker conditions. In this paper we extend these results to hyperbolic spaces
and directionally nonexpansive mappings. In particular, we obtain
significantly stronger and more general forms of the main results of a recent
paper by W.A. Kirk with explicit bounds. As a special feature of our
approach, which is based on logical analysis instead of functional analysis,
no functional analytic embeddings are needed to obtain our uniformity results
which contain all previously known results of this kind as special cases.
and even
weaker conditions. In this paper we extend these results to hyperbolic spaces
and directionally nonexpansive mappings. In particular, we obtain
significantly stronger and more general forms of the main results of a recent
paper by W.A. Kirk with explicit bounds. As a special feature of our
approach, which is based on logical analysis instead of functional analysis,
no functional analytic embeddings are needed to obtain our uniformity results
which contain all previously known results of this kind as special cases.
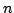 inputs, with high probability. The space needed to represent a function
is
inputs, with high probability. The space needed to represent a function
is 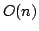 words, which is the best possible (and a polynomial improvement
compared to previous fast hash functions). As a consequence, a broad class of
hashing schemes can be implemented to meet, with high probability, the
performance guarantees of their uniform hashing analysis.
words, which is the best possible (and a polynomial improvement
compared to previous fast hash functions). As a consequence, a broad class of
hashing schemes can be implemented to meet, with high probability, the
performance guarantees of their uniform hashing analysis.
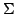 -formulas.
-formulas.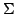 -predicates. It leads to a
topological characterisation of
-predicates. It leads to a
topological characterisation of 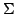 -relations on
-relations on 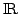 .
.
 -calculus and is intended for reasoning
about the behaviour of cryptographic protocols. We consider the
finite-control fragment of the spi-calculus, showing it to be Turing-powerful
(a result which is joint work with Josva Kleist, Uwe Nestmann, and Björn
Victor.) Next, we restrict our attention to finite (non-recursive)
spi-calculus. Here, we show that framed bisimilarity, an equivalence relation
proposed by Abadi and Gordon, showing that it is decidable for this fragment.
-calculus and is intended for reasoning
about the behaviour of cryptographic protocols. We consider the
finite-control fragment of the spi-calculus, showing it to be Turing-powerful
(a result which is joint work with Josva Kleist, Uwe Nestmann, and Björn
Victor.) Next, we restrict our attention to finite (non-recursive)
spi-calculus. Here, we show that framed bisimilarity, an equivalence relation
proposed by Abadi and Gordon, showing that it is decidable for this fragment.
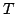 for
which each hom-set
for
which each hom-set 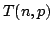 is a commutative monoid; composition on the right
distrbutes over all finite sums:
is a commutative monoid; composition on the right
distrbutes over all finite sums:
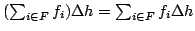 . A matrix theory is a grove theory in which composition on
the left and right distributes over finite sums. A matrix theory
. A matrix theory is a grove theory in which composition on
the left and right distributes over finite sums. A matrix theory 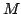 is
isomorphic to a theory of all matrices over the semiring
is
isomorphic to a theory of all matrices over the semiring 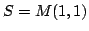 . Examples
of grove theories are theories of (bisimulation equivalence classes of)
synchronization trees, and theories of formal tree series over a semiring
. Examples
of grove theories are theories of (bisimulation equivalence classes of)
synchronization trees, and theories of formal tree series over a semiring
 . Our main theorem states that if
. Our main theorem states that if  is a grove theory which has a matrix
subtheory
is a grove theory which has a matrix
subtheory  which is an iteration theory, then, under certain conditions,
the fixed point operation on
which is an iteration theory, then, under certain conditions,
the fixed point operation on 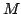 can be extended in exactly one way to a
fixedpoint operation on
can be extended in exactly one way to a
fixedpoint operation on 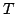 such that
such that 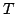 is an iteration theory. A second
theorem is a Kleene-type result. Assume that
is an iteration theory. A second
theorem is a Kleene-type result. Assume that 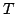 is a iteration grove theory
and
is a iteration grove theory
and 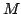 is a sub iteration grove theory of
is a sub iteration grove theory of 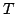 which is a matrix theory. For
a given collection
which is a matrix theory. For
a given collection 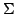 of scalar morphisms in
of scalar morphisms in 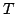 we describe the
smallest sub iteration grove theory of
we describe the
smallest sub iteration grove theory of 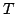 containing all the morphisms in
containing all the morphisms in
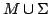 .
.
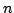 vertices. We present
an infinite family of graphs having
vertices. We present
an infinite family of graphs having
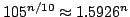 such
subgraphs, which improves an earlier lower bound by Schiermeyer (1996). We
show an upper bound of
such
subgraphs, which improves an earlier lower bound by Schiermeyer (1996). We
show an upper bound of
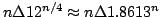 and give an
algorithm that lists all maximal induced bipartite subgraphs in time
proportional to this bound. This is used in an algorithm for checking
4-colourability of a graph running within the same time bound.
and give an
algorithm that lists all maximal induced bipartite subgraphs in time
proportional to this bound. This is used in an algorithm for checking
4-colourability of a graph running within the same time bound.
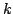 in any graph of size
in any graph of size  is at most
is at most
 . For maximal
independent sets of size at most
. For maximal
independent sets of size at most 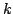 the same bound holds for
the same bound holds for 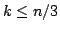 . For
. For 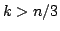 a bound of approximately
a bound of approximately 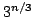 is given. All the bounds
are exactly tight and improve Eppstein (2001) who give the bound
is given. All the bounds
are exactly tight and improve Eppstein (2001) who give the bound
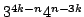 on the number of maximal independent sets of size at most
on the number of maximal independent sets of size at most
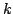 , which is the same for
, which is the same for
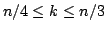 , but larger otherwise. We
give an algorithm listing the maximal independent sets in a graph in time
proportional to these bounds (ignoring a polynomial factor), and we use this
algorithm to construct algorithms for 4- and 5- colouring running in time
, but larger otherwise. We
give an algorithm listing the maximal independent sets in a graph in time
proportional to these bounds (ignoring a polynomial factor), and we use this
algorithm to construct algorithms for 4- and 5- colouring running in time
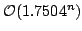 and
and
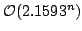 , respectively.
, respectively.
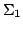 formulas in classical
analysis. As a second application of modified bar recursion we present a bar
recursive definition of the fan functional. Moreover, we show that modified
bar recursion exists in
formulas in classical
analysis. As a second application of modified bar recursion we present a bar
recursive definition of the fan functional. Moreover, we show that modified
bar recursion exists in  (the model of strongly majorizable
functionals) and is not S1-S9 computable in
(the model of strongly majorizable
functionals) and is not S1-S9 computable in  (the model of total
functionals). Finally, we show that modified bar recursion defines Spector's
bar recursion primitive recursively.
(the model of total
functionals). Finally, we show that modified bar recursion defines Spector's
bar recursion primitive recursively.
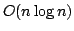 .
.
 such that given a query pattern of
length
such that given a query pattern of
length  , the maximum number of non-overlapping occurrences of the query
pattern in the string can be reported efficiently. Apostolico and Preparata
introduced the minimal augmented suffix tree (MAST) as a data structure for
the string statistics problem, and showed how to construct the MAST in time
, the maximum number of non-overlapping occurrences of the query
pattern in the string can be reported efficiently. Apostolico and Preparata
introduced the minimal augmented suffix tree (MAST) as a data structure for
the string statistics problem, and showed how to construct the MAST in time
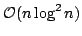 and how it supports queries in time
and how it supports queries in time 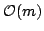 for
constant sized alphabets. A subsequent theorem by Fraenkel and Simpson
stating that a string has at most a linear number of distinct squares implies
that the MAST requires space
for
constant sized alphabets. A subsequent theorem by Fraenkel and Simpson
stating that a string has at most a linear number of distinct squares implies
that the MAST requires space 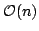 . In this paper we improve the
construction time for the MAST to
. In this paper we improve the
construction time for the MAST to
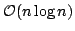 by extending the
algorithm of Apostolico and Preparata to exploit properties of efficient
joining and splitting of search trees together with a refined analysis.
by extending the
algorithm of Apostolico and Preparata to exploit properties of efficient
joining and splitting of search trees together with a refined analysis.
 in arbitrary normed spaces. We used this
result to obtain a new strong uniform version of Ishikawa's theorem for
bounded
in arbitrary normed spaces. We used this
result to obtain a new strong uniform version of Ishikawa's theorem for
bounded 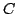 . In this paper we give a qualitative improvement of our result in
the unbounded case and prove the uniformity result for the bounded case under
the weaker assumption that
. In this paper we give a qualitative improvement of our result in
the unbounded case and prove the uniformity result for the bounded case under
the weaker assumption that 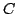 contains a point
contains a point 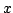 whose Krasnoselski-Mann
iteration
whose Krasnoselski-Mann
iteration 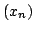 is bounded.
is bounded.
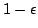 , and otherwise returns ``don't
know''. The lookup procedure uses an expander graph to select the memory
location to probe. Recent explicit expander constructions are shown to yield
space usage much smaller than what would be required using a deterministic
lookup procedure. Our data structure supports efficient deterministic
updates, exhibiting new probabilistic guarantees on dictionary running time.
, and otherwise returns ``don't
know''. The lookup procedure uses an expander graph to select the memory
location to probe. Recent explicit expander constructions are shown to yield
space usage much smaller than what would be required using a deterministic
lookup procedure. Our data structure supports efficient deterministic
updates, exhibiting new probabilistic guarantees on dictionary running time.
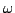 -)continuous or
monotonic functions, with three axiom schemas that express laws that are
specific to probabilistic bisimilarity. Hence probabilistic bisimilarity
(over finite-state agents) has an equational axiomatization relative to
iteration algebras.
-)continuous or
monotonic functions, with three axiom schemas that express laws that are
specific to probabilistic bisimilarity. Hence probabilistic bisimilarity
(over finite-state agents) has an equational axiomatization relative to
iteration algebras.
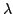 -calculus, and is due to Sabry
and Felleisen. To relate the two approaches, we use Church encoding,
Reynolds's defunctionalization, and an implementation technique for syntactic
theories, refocusing, developed in the second author's PhD thesis.
-calculus, and is due to Sabry
and Felleisen. To relate the two approaches, we use Church encoding,
Reynolds's defunctionalization, and an implementation technique for syntactic
theories, refocusing, developed in the second author's PhD thesis.