This document is also available as
PostScript
and
DVI.
- NS-95-6
-
Aravind Srinivasan.
The Role of Randomness in Computation.
November 1995.
iv+99 pp.
Abstract: The course was intended to serve both as a tutorial
introduction to the role of randomness in computation, specifically in
algorithms and complexity, and as a forum for the discussion of the most
recent research in the area. The course was organised into a sequence of 6
lectures:
- Introduction,
- Randomness in
Distributed Computing,
- Derandomisation,
- Random Sampling,
- The Lovasz Local Lemma,
- Weak Random Sources.
In
addition, the course was supplemented by a talk on ``Improved Approximation
Algorithms for Packing and Covering Problems''.
- NS-95-5
-
Robert Paige.
Analysis and Transformation of Set-Theoretic Languages.
Mini-Course.
August 1995.
iv+157 pp.
Abstract: The course was on how types and transformations can
be used to integrate algorithm design and analysis, program development, and
high level compilation of set theoretic programming languages. Topics:
- Introduction to SETL and sources of inefficiency;
program improvement by finite differencing,
- Program improvement by
real-time simulation of a typed set machine (equipped with high level
input/output) on a RAM,
- Reconstruction and extension of the linear time
fragment of Willard's database predicate retrieval theory,
- Design of A
linear time fixed point language; experiments in productivity of algorithm
implementation.
.
- NS-95-4
-
PostScript.
Yuri Gurevich and Egon Börger.
Evolving Algebras. Mini-Course.
July 1995.
iv+222 pp.
Abstract: Professors Egon Börger (Univ. of Pisa) and Yuri
Gurevich (Univ. of Michigan) visited BRICS during August 1995. From 7-10
August they held an intensive mini-course of 14 double lectures on Evolving
Algebras: their framework for modelling algorithms and languages, with links
to both Complexity Theory and Semantics. The background and interests of both
lecturers fitted particularly well with the BRICS idea of synergy between
Algorithms and Complexity Theory, Semantics, and Logic.
The course was
attended by 12 PhD students. Gurevich's lectures on the basic concepts and
definitions of evolving algebras were all prepared specially for the course,
and supported by a large collection of papers from the literature.
Börger's lectures on applications of evolving algebras were based on some
of his latest papers.
The course was organized by Peter D. Mosses.
BRICS is very grateful to the lecturers for their efforts, during what turned
out to be quite a hot week!
- NS-95-3
-
PostScript,
DVI.
Andrew D. Gordon.
Bisimilarity as a Theory of Functional Programming.
Mini-Course.
July 1995.
iv+59 pp.
Abstract: Operational intuition is central to computer science.
These notes introduce functional programmers to operational semantics and
operational equivalence. We show how the idea of bisimilarity from CCS may be
applied to deterministic functional languages. On elementary operational
grounds it justifies equational reasoning and proofs about infinite streams.
- NS-95-2
-
PostScript,
PDF.
Uffe H. Engberg, Kim G. Larsen, and Arne
Skou, editors.
Proceedings of the Workshop on Tools and Algorithms for The
Construction and Analysis of Systems, TACAS (Aarhus, Denmark, 19-20 May,
1995), May 1995.
vi+334 pp. Selected papers appears in Brinksma, Cleaveland, Larsen,
Margaria and Steffen, editors, Tools and Algorithms for The Construction
and Analysis of Systems: International Workshop, TACAS '95 Selected
Papers, LNCS 1019, 1995.
Abstract: The aim of the workshop on Tools and Algorithms
for the Construction and Analysis of Systems, TACAS, is to bring together
researchers and practitioners interested in the development and application
of tools and algorithms for specification, verification, analysis and
construction of distributed systems. The overall goal of the workshop is to
compare the various methods and the degree to which they are supported by
interacting or fully automatic tools.
The 23 papers of the proceedings
cover the following topics: refinement-based verification and construction
techniques; compositional verification methodologies; analysis and
verification via theorem-proving; decision procedures for verification and
analysis; specification formalisms, including process algebras and temporal
and modal logics; analysis techniques for real-time and/or probabilistic
systems; approaches for value-passing systems, tool sets for verification and
analysis case studies. There were special sessions for demonstration of
verification tools.
- NS-95-1
-
PostScript.
Igor Walukiewicz.
Notes on the Propositional 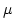 -calculus: Completeness and
Related Results. -calculus: Completeness and
Related Results.
February 1995.
54 pp.
Abstract: In this notes we consider propositional 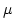 -calculus as introduced by Kozen. The main purpose of these notes is to
present the completeness proof of the Kozen's axiomatisation of the -calculus as introduced by Kozen. The main purpose of these notes is to
present the completeness proof of the Kozen's axiomatisation of the
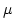 -calculus. To achieve this goal we develop tools which allow us to give
relatively simple proofs of results for the logic like: -calculus. To achieve this goal we develop tools which allow us to give
relatively simple proofs of results for the logic like:
- syntactic characterisation of satisfiability and validity,
- small model
theorem,
- decidability,
- equivalence of the
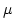 -calculus over
binary trees and Rabin automata, -calculus over
binary trees and Rabin automata,
- a notion of disjunctive formula and
the proof that every formula is equivalent to a disjunctive formula,
- linear satisfiability checking algorithm for disjunctive formulas.
These notes are intended to supplement a 6 hours course given
in February 1995 at BRICS centre.
|
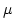 -calculus: Completeness and
Related Results.
-calculus: Completeness and
Related Results.
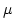 -calculus as introduced by Kozen. The main purpose of these notes is to
present the completeness proof of the Kozen's axiomatisation of the
-calculus as introduced by Kozen. The main purpose of these notes is to
present the completeness proof of the Kozen's axiomatisation of the
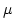 -calculus. To achieve this goal we develop tools which allow us to give
relatively simple proofs of results for the logic like:
-calculus. To achieve this goal we develop tools which allow us to give
relatively simple proofs of results for the logic like:
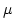 -calculus over
binary trees and Rabin automata,
-calculus over
binary trees and Rabin automata,